Difference between PV Valve and PV Breaker : The Pressure Vacuum (PV) Valve and the Pressure Vacuum (PV) Breaker are critical safety devices used on ships, especially on oil tankers, to regulate and maintain safe pressure levels within cargo tanks. While both devices play a role in preventing overpressure or vacuum conditions, they operate under different circumstances and serve different purposes.
What is pressure vacuum (PV Valve ) and pressure vacuum (PV ) Breaker ?
Pressure Vacuum (PV) Valve:
A Pressure Vacuum Valve (PV Valve) is a device used to maintain a balanced pressure in a cargo tank during loading, discharging, or transportation of cargo. It ensures that the tank does not experience dangerous overpressure or underpressure conditions, which could potentially lead to ruptures or implosions. The PV valve opens when the tank pressure exceeds the safe limit or falls below a certain threshold, allowing gases to escape or air to enter, keeping the tank safe and intact.
Pressure Vacuum (PV) Breaker:
A Pressure Vacuum Breaker (PV Breaker) is a safety device installed in the inert gas (IG) line on a ship’s deck. It ensures that the pressure in the system stays within safe limits, preventing the buildup of excessive pressure or creating a vacuum condition in the IG line. This is important for protecting the cargo tanks and the ship’s structure from potential damage. The PV Breaker acts as a backup for the PV Valve, ensuring additional safety by breaking any excessive vacuum or pressure in the system.It is a safety devices which is used in IG Line on Deck.
Function of pv valve and Pv breaker
Here are the functions of both the Pressure Vacuum (PV) Valve and the Pressure Vacuum (PV) Breaker:
Functions of PV Valve:
- Maintaining Pressure and Vacuum: The PV valve ensures that the cargo tank maintains a balanced pressure during loading and unloading operations.
- Preventing Overpressure: It releases excess pressure from the tank to prevent overpressure conditions, which could damage the tank.
- Preventing Underpressure: It allows air or gas to enter the tank to prevent underpressure (vacuum) conditions that could collapse the tank.
Functions of PV Breaker:
- Handling Abnormal Pressure Increases During Loading: The PV breaker opens to relieve abnormal pressure increases when the gas outlet rate from the tank is insufficient during cargo loading.
- Handling Abnormal Pressure Increases During Discharge: When cargo is discharged at a higher rate than the inert gas blower can replace, the PV breaker prevents pressure buildup in the tank.
- Dealing with Breather Valve Malfunction: In case the breather valve fails to operate due to pressure fluctuations (caused by changes in atmospheric or seawater temperatures), the PV breaker steps in to stabilize the tank’s pressure, either releasing or admitting gas as necessary.
Both devices are crucial for maintaining safe operating conditions within cargo tanks.
Difference Between PV Valve and PV Breaker
Let’s break down the key differences between the PV Valve and the PV Breaker from various points of comparison.
Overview:
The Pressure Vacuum (PV) Valve and the Pressure Vacuum (PV) Breaker are critical safety devices used on ships, especially on oil tankers, to regulate and maintain safe pressure levels within cargo tanks. While both devices play a role in preventing overpressure or vacuum conditions, they operate under different circumstances and serve different purposes. Let’s break down the key differences between the PV Valve and the PV Breaker from various points of comparison.
Difference between PV Valve and PV Breaker:
| Point of Comparison | PV Valve | PV Breaker |
|---|---|---|
| Function | Maintains safe pressure and vacuum in individual cargo tanks during normal operations such as loading and unloading. | Handles abnormal increases in pressure or vacuum when the PV valve is unable to cope, providing backup for excessive pressure surges. |
| Location | Installed on each cargo tank individually. | Installed on the inert gas (IG) line on the deck, serving all cargo tanks. |
| Operating Pressure | Operates at 1400 mm of water column (0.14 bar) and vacuum of -250 mm of water column (-0.025 bar). | Operates at 1600 to 1800 mm of water column (0.16 to 0.18 bar) and vacuum of 400 mm of water column (-0.04 bar). |
| Primary Role | Ensures normal pressure control in the cargo tank during loading, discharging, and transportation. | Acts as a safety backup when pressure or vacuum exceeds the PV valve’s capacity, preventing dangerous tank conditions. |
| Handling Rate of Loading | Handles pressure adjustments during normal cargo loading and discharging rates. | Handles rapid and abnormal increases in pressure due to fast loading rates or equipment failure. |
| Response to Vacuum | Opens to let air into the tank if vacuum conditions occur, ensuring the tank doesn’t collapse. | Operates when the vacuum exceeds the PV valve’s limits to protect the system from extreme vacuum conditions. |
| Number of Devices | Typically, one PV valve per cargo tank. | Typically, only one PV breaker per system, serving all tanks via the IG line. |
| Design Objective | Primarily designed for normal operational safety. | Designed to handle emergency situations when the pressure exceeds normal levels or when equipment (like the breather valve) malfunctions. |
On basis of operating pressure
Based on the operating pressures measured in terms of water column (mm of water column):
Pressure Vacuum (PV) Valve:
- Operating Pressure:
- The PV valve operates at 1400 mm of water column (which is approximately 0.14 bar).
- It also operates at a vacuum of -250 mm of water column (approximately -0.025 bar). This means the valve opens to relieve pressure when it reaches 1400 mm water column and allows air in when the vacuum reaches -250 mm.
Pressure Vacuum (PV) Breaker:
- Operating Pressure:
- The PV breaker operates between 1600 mm to 1800 mm of water column (which is approximately 0.16 to 0.18 bar).
- It operates at a vacuum of 400 mm of water column (approximately -0.04 bar). The PV breaker is designed to activate when the pressure or vacuum exceeds the capacity of the PV valve, handling higher pressure surges or stronger vacuum conditions.
Conversion Note:
As a reference:
- 1000 mm of water column ≈ 0.1 bar
This helps in converting between pressure in mm of water column and bar as needed.Image
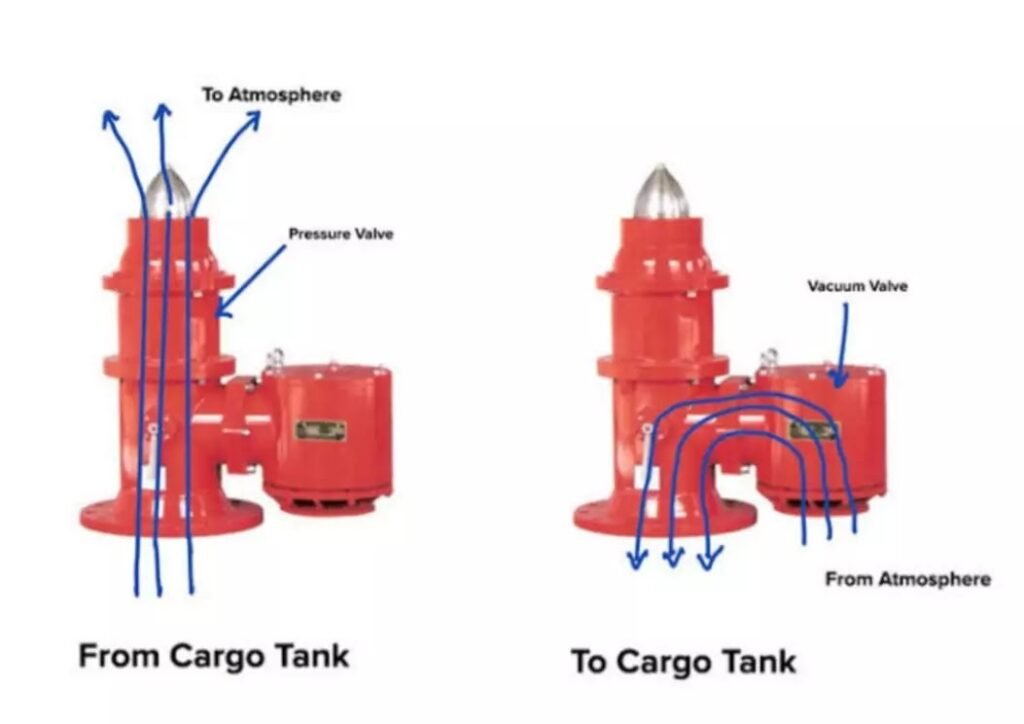
When and where Pv breaker and pv valve is used
Where and When PV Valve is Used:
- Location: An individual PV Valve is installed on each cargo tank. It directly controls the pressure and vacuum within that specific tank.
- Usage:
- During loading and unloading operations, where pressure fluctuations can occur.
- The PV valve automatically responds to minor pressure or vacuum changes in the tank. If the internal pressure drops below a certain level, the valve opens downward, allowing external air or gas to enter the tank. If the pressure inside the tank exceeds a certain limit, the valve opens upward, allowing gases to escape.
- It works under normal operating conditions to maintain the balance between internal and external pressure.
Where and When PV Breaker is Used:
- Location: Typically, only one PV breaker is fitted in the inert gas (IG) line on the deck of the ship, servicing all cargo tanks through the IG system.
- Usage:
- The PV breaker is used in situations where there is an abnormal pressure increase that exceeds the handling capacity of the PV valve.
- This occurs when cargo is loaded at a high rate, causing a rapid increase in pressure that could lead to an explosion if not relieved.
- The PV breaker opens to relieve the excess pressure when the loading rate or inert gas blower is beyond the specified limit.
- It also activates if there is a malfunction in the PV valve or breather valve, ensuring the safety of the cargo tanks.
In essence, PV valves handle normal operational pressure adjustments, while the PV breaker acts as a safety backup for extreme pressure surges.
What pressure it maintains
The pressure ranges maintained by the PV Valve and PV Breaker are as follows:
PV Valve:
- Pressure Range:
- For large oil tankers, the PV valve typically maintains the tank pressure between 0.07 to 0.20 bar.
- It ensures that minor pressure fluctuations are controlled, keeping the tank pressure within this range during normal operations like loading and unloading.
PV Breaker:
- Pressure Handling:
- The PV breaker is designed to handle pressure surges beyond the capacity of the PV valve.
- It activates if the pressure rises to 0.24 bar (maximum), relieving the excess pressure and preventing any damage to the cargo tanks.
In summary, the PV valve handles normal pressure regulation, while the PV breaker comes into play when the pressure rises abnormally, ensuring safety beyond the operational limits of the PV valve.
Summary
- The PV valve manages everyday pressure and vacuum conditions within each cargo tank, ensuring safe operations during cargo loading and unloading.
- The PV breaker steps in during emergency situations when pressure or vacuum conditions become abnormal, acting as a secondary safeguard for the entire cargo system.
Also Read : Bearing Temperature Detector
You Can Read More About It On, https://www.quora.com/unanswered/What-is-the-difference-between-a-PV-breaker-and-a-deck-seal-on-a-tanker-vessel
Check Out Other Important Topics
