Overview
A starting air line explosion refers to an explosive event that occurs within the starting air system of a diesel engine or gas turbine, typically during the starting process. This can happen in marine engines, power plants, or any system where compressed air is used to start internal combustion engines. Here’s an overview of what it entails:
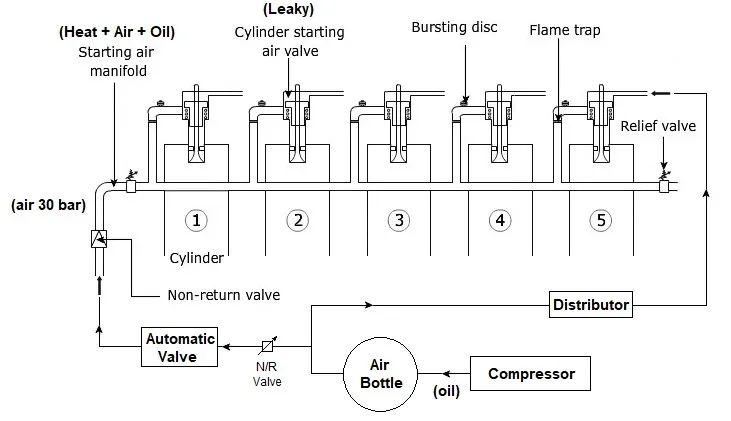
What is starting air line explosion ?
Explosion: An explosion in this context refers to a sudden and violent release of energy, resulting from the ignition of combustible mixtures (such as compressed air mixed with oil or other flammable materials) or the failure of components due to excessive pressure.
Starting Air Line: This is the system consisting of pipes, valves, and storage tanks that supply compressed air to the engine for starting. The air serves to turn the engine over, allowing it to begin combustion.
Hence, Explosion in the air starting line due to fire occur in the starting air line of main engine.
How starting air line explosion takes place ?
Starting air line explosions occur when the conditions of the fire triangle are met: Oxygen, Heat, and Fuel. Here’s how these elements come together in the context of a starting air line explosion.
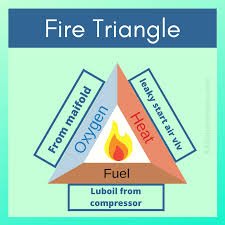
Fire Triangle Components
1. Oxygen: In the starting air line or manifold, compressed air serves as the source of oxygen. This air is present in bulk, often at high pressures (around 30 bar), facilitating combustion when mixed with fuel.
2. Heat Source: A heat source is critical for ignition. In the context of a starting air line, heat can arise from several sources:
- Leaky Air Starting Valve: If the valve leaks, it may allow compressed air to escape, creating friction and heat.
- Engine Operation: During engine operation, exhaust heat and other operational factors may contribute additional heat.
3. Fuel: The presence of lube oil is crucial. Despite the air being predominantly nitrogen and oxygen, it is not pure. The air may carry a certain amount of oil mist due to:
- Main Air Compressor: This compressor generates the high-pressure air required for starting. Lube oil used for the lubrication of the liner and piston can mix with the compressed air due to wear or improper maintenance.
- Combustible Mixture: This mixture of air and oil creates a combustible fuel source. When the oil is aerosolized into tiny droplets suspended in the air, it becomes highly flammable.
How oil come in the air of air starting line ?
Main air compressor used to produce 30 Bar. Lube oil used for lubrication of liner and piston. Some amount of lube oil mix with air. This air finally come to air starting manifold become combustible liquid for explosion.
Combustible fuel is available as lube oil carried out from main air compressor. Oxygen is available in bulk. Due to leaky air starting valve heat from combustion chamber igniters the lube oil, Thus Starting air line explosion Occur.
What are the causes of starting air line Explosion ?
- Leaky Starting Air Valve: When the starting air valve leaks, it can allow pressurized air to escape, creating a situation where excess air accumulates. This can lead to overpressure in the system or the introduction of air into unintended areas, raising the risk of an explosion.
- Stuck Open Air Starting Valve: If the air starting valve becomes stuck in the open position, it can lead to continuous airflow into the combustion chamber or other parts of the engine. This not only affects engine performance but can also create hazardous pressure levels, leading to potential explosions.
- Oil Contamination: Oil from the main air compressor can mix with the compressed air if the oil separator is not functioning correctly. This mixture can become combustible, posing a significant explosion risk when combined with high-pressure air and potential ignition sources.
- High Compressed Air During Maneuvering: maneuvers, if high-compressed air interacts with unintended sources of ignition (such as electrical sparks or hot surfaces), it can ignite, leading to an explosion. This is particularly critical when operating in enclosed or poorly ventilated areas.
- Moisture Accumulation: Water or moisture in the air lines can lead to corrosion and weakening of the components, potentially causing leaks or ruptures. If this moisture becomes contaminated with oil, the risk of explosion increases.
- Component Failures: Failures in other components such as pressure relief valves, hoses, or pipes due to wear and tear can lead to sudden releases of air under high pressure, creating dangerous situations.
Preventive measures of starting air line explosion
Preventing an explosion in the starting air line requires a comprehensive approach to maintenance, monitoring, and operational practices. Here are key preventive measures:
1.Maintain Main Air Compressor:
- Ensure that the main air compressor is in good working condition. Regular maintenance should include checking oil levels, seals, and any wear and tear on components.
- Verify that the lubrication system is sufficient, including checking that the feed rate of lube oil is adequate for the compressor’s cylinders.
2.Regular Draining of Air Bottles:
- Drain the air bottles at least once every watch. This helps to remove any accumulated moisture or contaminants that could compromise system integrity.
- Ensure that the drained fluid is disposed of properly to prevent environmental contamination.
3.Drain Air Starting Line/Manifold:
- Drain the air starting line or manifold when the engine is stopped, allowing any built-up moisture or debris to escape. This reduces the risk of corrosion and pressure imbalances that could lead to failures.
4.Regular Overhaul of Air Starting Valves:
- Conduct regular overhauls of the air starting valves for each cylinder. This maintenance helps ensure that the valves are functioning correctly, sealing properly, and not leaking pressurized air.
5.Leak Testing of Air Starting Valves:
- Perform leak tests on the air starting valves before departure to ensure that they are not leaking. Utilization of proper testing techniques can identify potential failures before they result in catastrophic events.
6.Monitor Oil Separator Function:
- Ensure that the oil separator at the discharge side of the main air compressor is operating effectively. This component is critical for separating and removing oil from compressed air, preventing oil from contaminating the air supply. Regular checks and maintenance of the oil separator are essential.
7.Inspect Pressure Relief Valves:
- Regularly inspect and test pressure relief valves to ensure they are operational. These valves help protect the air starting system from overpressure situations that could lead to explosions.
By adhering to these preventive measures, the risk of starting air line explosions can be significantly reduced, enhancing safety and operational efficiency.
what are the safety devices fitted on starting air line to prevent Explosion?
1.Flame arrestor :- It is fitted before air stating valve for each cylinder in the air starting pipe. A flame arrestor is a device which allow to pass a gas through it and did the work of stopping a propagation of flame. or, It is a small unit or device which consist of many tubes which arrest any flame or spark coming from the cylinder due to leaky air starting valve.
2.Bursting Disc :- Bursting disc is installed in the starting air pipe and consists of a perforated disc protected by a sheet of materials that will burst in the event of an air line explosion. It also includes a protective cap that is designed in such a way that if the engine is required to run even after the disc has been ruptured, the cap will cover the holes when turned. This ensures that manoeuvring or traffic air is always available to the engine.
Bursting discs are pressure relief devices with a defined breaking point that respond to a specific pressure and are used in a wide range of applications. They are used to protect against overpressure or vacuum within a process, thereby protecting man, the environment, and the machine. It is also known as rupture discs , Burst disk and diaphagram disk.
3.Non return valve :- Because of the unidirectional property of the non-return valve, it will not allow the explosion and its mixture to reach the air bottle if it is located between the Air Manifold and the Air Receiver.
4.Relief Valve :- It is installed on the common air manifold, which provides air to the cylinder head. It is normally installed at the end of the manifold and lifts the valve if there is too much pressure inside the manifold. The benefit of a relief valve is that it will sit back after removing the excess pressure, allowing continuous air to be available to the engine in the event of manoeuvring or traffic.
5.Air starting manifold drain :- Drain the manifold of starting air when engine is stopped.
How will you know your air starting valve is leaking
To determine if your air starting valve is leaking, different methods can be employed depending on whether the engine is running or stopped. Here’s a comprehensive overview:
1. When the Engine is Running
In this scenario, there are several indicators of a potential leak in the air starting valve:
- Heat in the Air Starting Line: If there’s a leak, the air starting line or manifold may become excessively hot due to the escaping compressed air. You can assess this by carefully touching the line; if it feels hot to the touch or red hot, it indicates a significant leak.
- Relief Valve Activity: The relief valve, installed at the end of the air starting manifold, may lift repeatedly due to overpressure from the leakage. This will typically be accompanied by a loud sound, indicating that it is functioning to relieve excessive pressure caused by the leak.
- Bursting Disc Failure: If the leaking continues to escalate, the bursting disc situated along the air starting line might burst. This failure leads to a rapid release of pressure, indicating a serious issue with the air starting system.
- Smoke from the Drain: Observing smoke or vapors emerging from the drain fitted in the air starting manifold also suggests that there is an air leak. This could indicate that the leakage is causing abnormal operation, affecting the temperature and pressure in the system.
2. When the Engine is Stopped
In the case of the engine being stopped, identifying a leak requires a different approach:
- Presence of Air in the Cylinder: When the engine is not running, the air in the starting line is still present. If there’s a leak in the starting valve, air from the manifold can leak into the combustion chamber.
- Using the Indicator Valve: To check for leaks, you can open the indicator valve. If there is leakage, you will hear a rush of air escaping as it begins to fill the cylinder with air from the manifold. This signifies that the air starting valve is leaking and not sealing correctly.
Monitoring both the operational state of the engine and the physical attributes of the air starting system can effectively determine if the air starting valve is leaking. Regular inspections, along with awareness of the discussed symptoms, can ensure the proper functioning of the air starting system and help avoid unexpected failures.
Why negative cam is provided in air starting Distributor ?
The use of a negative cam in an air starting distributor serves multiple critical purposes related to safety and the operational reliability of the air starting system. Here’s a breakdown of why a negative cam is provided:
1. Positive Closure of Stuck Valves : The negative cam ensures that if the air starting valve becomes stuck in an open position, the cam design will trigger a positive closure. This is crucial for safety, as it prevents the engine from starting unintentionally due to a malfunction.
2. Preventing Valve Activation without Pilot Air
Blocking Access Without Pilot Air: When someone attempts to open the air starting line from the air bottle without the necessary pilot air pressure, the negative cam design prevents the valve from opening. This ensures that all rollers are lifted, and the valve remains closed, thereby preserving system integrity and safety.
3.Protection During Engine Operation
Continuous Roller Lift: While the main engine operates, the negative cam allows all rollers of the air distributor to remain lifted due to spring action. This means that as the cam rotates, there is no wear on the rollers because they are not in contact with the cam surface. This reduces maintenance requirements and extends the life of the components.
4.Reduced Wear and Tear
Minimized Component Wear: Because the negative cam keeps the rollers lifted during normal operating conditions, it prevents unnecessary wear. This is critical in maintaining the reliability and efficiency of the starting system over time.
Action in case of starting air line explosion
- Notify the Bridge: Quickly tell the bridge (the control room) about the explosion.
- Stop the Engine: Ask them to turn off the engine if it’s safe to do so. If they can’t stop it, move to the next step.
- Cut Off Fuel Supply: If the engine can’t be stopped, turn off the fuel supply to the cylinder that might catch fire. This helps prevent a fire.
- Prepare for Valve Replacement: Get the new air starting valve ready to replace the broken one as soon as you can.
- Monitor the Situation: Keep watching what’s happening and stay in touch with the bridge and the crew to keep everyone informed.
- Follow Safety Guidelines: Make sure to follow all safety rules while handling the situation.
- Investigate Later: Once everything is under control, look into what caused the explosion and find ways to prevent it from happening again.
This plan will help you respond quickly and safely if there’s an explosion.
Check Out Other Important Topics
| IC Engine | Important PDFs | Boilers | Synergy Maritime Exam | Naval Arch | MEO Class 4 |
| Interview Questions | Difference Between | Types of Pumps | Auxiliary Machines | Types of Valves | Home |
