In this article, I am going to explain about refrigeration cycle in details like definition of Refrigeration, What are the 4 cycles of the refrigeration system? What is the principle of refrigeration? What are the parts of refrigerator? Refrigeration cycle diagram and working. Before starting first understand the term refrigeration.
What is Refrigeration ?
Refrigeration means cooling a space, substance or system to lower and/or maintain its temperature below the ambient one (while the removed heat is rejected at a higher temperature). In other words, refrigeration is artificial (human-made) cooling.
What is Refrigeration Cycle ?
Refrigeration cycle is a cycle of mechanical system in which transmission of heat flow from one place at a lower temperature (the source ) to another place at a higher temperature ( the sink or heat sink ) by continuously circulating, evaporating, and condensing a fixed supply of refrigerant in a closed system.
Refrigeration cycle is a thermodynamic cycle to generate refrigerating effect with the use of evaporator, compressor, condenser & expansion valve.
Refrigeration cycle name – It is also called heat pump cycle .
Thus, a heat pump is called as a “heater” if the objective is to warm the heat sink (as when warming the inside of a home on a cold day), or a “refrigerator” or “cooler” if the objective is to cool the heat source (as in the normal operation of a freezer).
In both cases, the working principles are same. Heat is removed from a cold place to a warm place. Below given is the refrigeration cycle diagram :
Refrigeration Cycle Diagram

Vapour Compression Cycle
Vapour Compression Refrigeration system is the most widely used refrigeration system.
Vapour compression refrigeration cycle is a process that uses the physics of phase change heat transfer and the unique properties of a refrigerant to transfer heat from a relatively cold source to a hot medium.
What is the Basic Refrigeration Cycle ?
The basic components of any refrigeration system working on the vapour compression cycle are the compressor, condenser, expansion valve and evaporator and the refrigerant fluid which is alternatively vaporized and liquefied during the refrigeration cycle.
The temperature at which a fluid boils or condenses is known as the saturation temperature .
Components of Refrigeration Cycle
The 4 main Components of Refrigeration cycle
1. Compressor
2. Condenser
3. Expansion valve
4. Evaporator
Refrigeration Cycle Working
Working of vapour compression refrigeration system has been explained step by step including the work done by each component in the cycle and can be seen in the refrigeration cycle diagram also.
1. Compressor
The compressor in a vapor compression cycle helps in raising the pressure of the vaporizer refrigerant, causing its saturation temperature to rise, so that it is higher than that of the the sea water or air, cooling the condenser. The compressor also promotes circulation of refrigerant by pumping it around the system.
Note :- Refrigerant enters the compressor as low-pressure, low-temperature gas, and leaves the compressor as a high-pressure, high-temperature gas.
Why compression takes place :- Compression takes place to raise the saturation temperature and refrigerant pressure.
2. Condenser
In the condenser of the vapour compression system the refrigerant is liquefied by being subcooled to below the saturation temperature relating to the compressor delivery pressure, by the circulating sea water or air for domestic refrigerator.
Latent heat, originally from the evaporator, is then transferred to the cooling medium. The liquid refrigerant, still at the pressure produced by the compressor, passes to the receiver and then to the expansion valve.
Note :- After condensing, the refrigerant is a high-pressure, low-temperature liquid, at the point it’s routed to the loop’s expansion device.
What happens in condenser :- Heat is transferred from the refrigerant to a flow of water
3. Expansion valve
The expansion valve is the regulator through which the refrigerant flow from the high pressure side of the system to the low pressure side. Its throttling effect dictates the compressor delivery pressure which must be sufficient to give the refrigerant a saturation temperature which is higher than the temperature of the cooling medium.
The pressure drop through the regulator causes the saturation temperature of the refrigerant to fall so that it boils at low temperature of the evaporator. In fact, as the liquid passes through the expansion valve, the pressure drop makes its saturation temperature fall below its actual temperature.
Some of the liquid boils off at the expansion valve taking latent heat from the remainder and causing it’s temperature to drop.
The expansion valve throttles the liquid refrigerant and maintains the pressure difference between the condenser and evaporator, while supplying refrigerant to the evaporator at the correct rate. It is thermostatically controlled in modern systems.
What happens to refrigerant in Expansion valve :- When the refrigerant enters the throttling valve, it expands and releases pressure. Consequently, the temperature drops at this stage.
4. Evaporator
The refrigerant entering the evaporator coil at a temperature lower than that of the surrounding. Secondary coolant (air or brine ) receives latent heat and evaporates. Later the heat is given off in the condenser, where the refrigerant is again compressed and liquefied.
Note :- Refrigerant enters the evaporator as a low temperature liquid at low pressure, and a fan forces air across the evaporator’s fins, cooling the air by absorbing the heat from the spaces.
What happens to refrigerant in evaporator :- It evaporates and absorbs latent heat of vaporization.
For a small refrigerator the evaporator cools without forced circulation of secondary coolant. In larger installation, the evaporator cools air or brine which are circulated as secondary refrigerants.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the refrigeration cycle called?
Refrigeration cycle is also called heat pump cycle
What are the 4 cycles to the refrigeration system?
The 4 main Components of Refrigeration cycle are :
1. Compressor
2. Condenser
3. Expansion valve
4. Evaporator
What Are the Different Types of Refrigeration Systems?
There are four main refrigeration cycle types :
1. Mechanical Compression Refrigeration System
2. Absorption Refrigeration
3. Evaporative Cooling
4. Thermoelectric Refrigeration
Which gas is used in refrigerator?
Tetrafluoroethane:
HFC-134a (1,1,1,2-Tetrafluoroethane) is one of the commonly used refrigerant gases which you can find in almost all the present time refrigerators.
we have covered all the required details of Refrigeration cycle ( vapour compression refrigeration system, vapour compression cycle, heat pump cycles ). This is the most basic refrigeration cycle and is known by many different names as mentioned. We got refrigeration cycle explained with the help of refrigeration cycle diagram and learned the thermodynamics of refrigeration.
For Better Explanation
Refrigeration Cycle Explained on YouTube
Check Out Other Important Topics

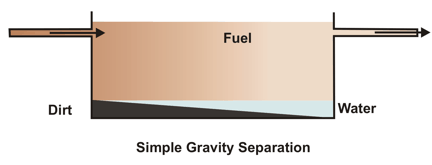 Basic principle of separation of water and impurities from fuel is gravity difference.
Basic principle of separation of water and impurities from fuel is gravity difference. When a bowl containing impure fuel is rotated, the centrifugal forces throw any item with a density greater than the density of fuel oil (solids and free water) to the bowl ‘s periphery.
When a bowl containing impure fuel is rotated, the centrifugal forces throw any item with a density greater than the density of fuel oil (solids and free water) to the bowl ‘s periphery.
 While in operation, a quantity of oil remains in the bowl to form a complete seal around the underside of the top disk and, due to the difference in density, the oil is confined to the outer diameter of the top disk.
While in operation, a quantity of oil remains in the bowl to form a complete seal around the underside of the top disk and, due to the difference in density, the oil is confined to the outer diameter of the top disk.