Welcome to this guide on butt welding, a popular joining technique used in metalworking. If you’re looking to enhance your skills in metal fabrication, mastering butt welding is essential. In this section, we will explore the basics of butt welding, its advantages, applications, and tips for achieving successful welds.
So whether you’re a seasoned metalworker looking to improve your skills or a beginner exploring welding techniques, this guide is for you. Let’s dive into the world of butt welding and discover how it can take your metalworking projects to the next level.

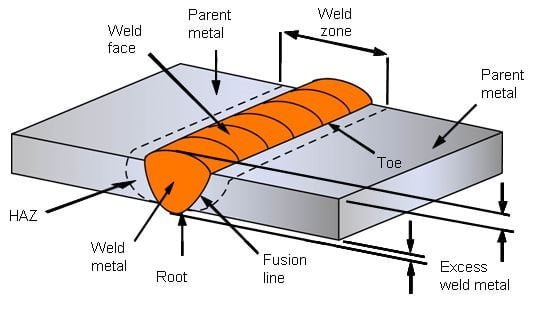
What is Butt Welding?
Butt welding is a technique used in metalworking that involves joining two pieces of metal along their edges to form a permanent bond. This is achieved by heating the metal to its melting point and then allowing it to cool and solidify, fusing the two pieces together. It is a popular method for creating strong and durable connections in a wide range of metalworking applications.
| Principles | Equipment | Materials |
|---|---|---|
| Butt welding involves joining two metal pieces along their edges through heat and pressure, creating a strong and permanent bond. | A butt welding machine is required to provide the necessary heat and pressure for the weld. Different machines are available depending on the specific application and materials involved. | The type of metal used in the welding process will depend on the specific application. Common materials include steel, aluminum, copper, and others. |
Butt welding can be used to join metal pieces of different sizes and thicknesses, making it a versatile joining method. The weld can also be made almost invisible, producing a clean and aesthetically pleasing finish.
With an understanding of the principles, equipment, and materials involved, we can now delve deeper into butt welding techniques and applications.
Butt Welding Fittings
Butt welding fittings are an essential component in butt welding applications. These fittings come in a variety of shapes, sizes, and materials to suit different metalworking projects. They are designed to connect two or more pipes or tubes in a seamless and permanent bond. Butt welding fittings are commonly made of stainless steel, carbon steel, or other alloys, depending on the application requirements.
The primary function of butt welding fittings is to provide a smooth and continuous flow of fluid or gas through the connected pipes or tubes. They are used in a range of industries, including oil and gas, chemical processing, power generation, and construction.
Some of the most common types of butt welding fittings include:
| Type of Fitting | Description |
|---|---|
| Elbow | Curved fitting that changes the direction of the pipe or tube |
| Tee | T-shaped fitting that splits the flow of fluid or gas into two directions |
| Reducer | Fitting that connects pipes or tubes of different sizes |
| Coupling | Fitting that connects two pipes or tubes of the same size |
Choosing the right butt welding fittings is crucial for achieving successful welds. The fittings should match the size, material, and purpose of the pipes or tubes being connected. Proper alignment and preparation of the edges are also essential for creating strong and durable welds.
Whether you are working on a small DIY project or a large-scale industrial application, selecting the right butt welding fittings is key to the success of your project.
Butt Welding Clamps
Clamping is an essential part of butt welding, as it helps to secure the workpieces and maintain proper alignment during the welding process. Choosing the right type of clamp is crucial for achieving successful welds.
There are various types of butt welding clamps available, including C-clamps, locking pliers, and magnetic clamps. C-clamps are the most common type of clamp and are suitable for most applications. They can be adjusted for different materials and thicknesses and are relatively easy to use. Locking pliers, on the other hand, provide a more secure grip but can be more challenging to position correctly. Magnetic clamps are useful for holding non-ferrous materials or in situations where traditional clamps cannot be used.
When using butt welding clamps, it’s essential to ensure that the workpieces are properly aligned, and there is sufficient pressure to hold them in place. The clamps should be positioned at equal distances along the joint, with enough clearance for the welding torch to pass through without hitting them. It’s also crucial to ensure that the clamps don’t interfere with the welding process and that they are removed immediately after welding to avoid distortion.
Overall, selecting the appropriate clamps and using them correctly is critical for achieving successful butt welds. Good clamping practices can help to prevent gaps, porosity, and other defects that can weaken the weld and compromise its integrity.
Flash Butt Welding
Flash butt welding is an advanced technique that involves utilizing the heat generated by an electric current to create strong welds. This process is commonly used in the automotive and aerospace industries, where precision and durability are critical.
How It Works
Flash butt welding works by using a clamping system to hold the two workpieces in place. An electric current is then applied between the two pieces, generating heat as the current flows through them. The heat causes the ends to melt and fuse together, creating a strong bond.
During this process, a flash is created as the welded pieces melt and come together. This flash is then trimmed off, leaving a clean and precise weld joint.
Advantages and Limitations
One of the main advantages of flash butt welding is the precision and control it offers. This method produces high-quality welds that are strong and durable.
Another advantage is the ability to control the heat input, which can be beneficial when working with materials that are sensitive to heat.
However, there are some limitations to flash butt welding. It requires specialized equipment and trained operators, and it may not be suitable for all materials.
Applications
Flash butt welding is used in a variety of applications, including the manufacture of automotive and aerospace components, such as axles and drive shafts.
This method is also used in the production of railway tracks, where it creates strong and durable connections between the rails.
Butt Welding Machine
Butt welding machines are specialized tools used to join two pieces of metal along their edges through a permanent bond. These machines use a variety of techniques to create high-quality and durable welds, making them popular in many industries.
There are different types of butt welding machines to choose from, including manual, semi-automatic, and fully automatic machines. Manual butt welding machines require an operator to manually control the welding process, while semi-automatic and fully automatic machines are more automated and allow for greater precision and efficiency.
Manual butt welding machines are suitable for small-scale projects and repairs, while semi-automatic and fully automatic machines are ideal for large-scale industrial projects. These machines come in various sizes and capabilities, so it is important to choose the right machine for the project at hand.
Butt welding machines typically consist of a welding head, clamping system, and welding control unit. The welding head aligns and joins the workpieces, while the clamping system holds them securely in place. The welding control unit regulates the temperature and time of the welding process for consistent and accurate results.
Regular maintenance of butt welding machines is crucial for their optimal performance and longevity. This includes cleaning, lubricating, and replacing parts as needed. It is also important to follow safety guidelines and use proper protective gear when operating butt welding machines.
Types of Butt Welding Machines
Here are some of the common types of butt welding machines:
| Type | Description |
|---|---|
| Manual Butt Welding Machine | A basic machine that requires an operator to manually control the welding process. Suitable for small-scale projects and repairs. |
| Semi-Automatic Butt Welding Machine | A more automated machine that uses a motorized clamping system and a control unit to regulate the welding process. Suitable for medium-scale industrial projects. |
| Fully Automatic Butt Welding Machine | A highly automated machine that uses advanced control systems and sensors to regulate the welding process. Ideal for large-scale industrial projects with high production volumes. |
Each type of butt welding machine has its own advantages and limitations, and choosing the right machine depends on the specific requirements of the project.
In conclusion, butt welding machines are essential tools for creating high-quality and durable welds in metalwork. By understanding the different types of machines available and their features and capabilities, metalworkers can choose the most suitable machine for their project and achieve optimal results.
Tips for Successful Butt Welding
Butt welding can produce strong and durable connections in metalwork when done correctly. Below are some tips to help ensure successful butt welds:
- Prepare the workpieces: Before welding, ensure that the surfaces to be joined are free of any dirt, oil, or rust. Use a wire brush or grinder to remove any contaminants.
- Choose the right joint design: The joint design can affect the strength and appearance of the weld. Butt joints, T-joints, and lap joints are some common designs. Choose the one that’s suitable for the intended application.
- Control the temperature: Maintaining the right temperature is crucial for successful butt welding. Use a heat source that’s suitable for the metal being joined. Monitor the temperature and adjust the settings as needed.
- Ensure proper alignment: Misaligned workpieces can lead to weak welds. Use clamps, jigs, or fixtures to hold the workpieces in place during welding. Check for alignment frequently.
- Weld in stages: Butt welding is best done in stages rather than all at once. Weld a short section and then let it cool before continuing. This can prevent warping and distortion of the workpieces.
- Use the right filler metal: The choice of filler metal can affect the strength and appearance of the weld. Match the filler metal to the base metal being welded.
- Practice: Butt welding requires skill and practice to master. Start with simple projects and work your way up to more complex ones.
By following these tips, you can achieve high-quality butt welds that are strong, durable, and aesthetically pleasing.
application of butt welding
Butt welding is a widely used welding technique with numerous applications across various industries. Some of the common applications of butt welding include:
- Pipeline Construction: Butt welding is extensively used in the oil and gas industry for joining sections of pipelines. It creates strong and leak-free connections, ensuring the safe transportation of fluids over long distances.
- Automotive Manufacturing: In the automotive industry, butt welding is used to join components like exhaust pipes, chassis parts, and body panels. It provides structural integrity and helps reduce vehicle weight.
- Aerospace: Butt welding is used in the aerospace industry to fabricate components for aircraft and spacecraft, where lightweight, high-strength, and reliable joints are essential.
- Shipbuilding: Shipbuilders use butt welding to join steel plates and structural components in the construction of ships and offshore structures, ensuring the integrity of the vessel’s hull.
- Pressure Vessels: Butt welding is employed in the fabrication of pressure vessels, such as boilers and tanks, where the welds must withstand high pressures and temperatures.
- Construction: In construction, butt welding is used for structural steel fabrication, creating beams, columns, and other load-bearing elements. It also finds use in architectural applications for clean and aesthetically pleasing joints.
- Piping Systems: Butt welding is crucial in the installation of plumbing and HVAC systems. It ensures leak-free connections for water, gas, and air distribution.
- Power Generation: In power plants, butt welding is used for assembling and repairing components in boilers, heat exchangers, and turbines, where high-temperature and high-pressure conditions exist.
- Railroad Industry: Butt welding is employed in the manufacturing and maintenance of railway tracks and components like rails and switches, ensuring safe and reliable train operations.
- Manufacturing Equipment: Butt welding is used in the fabrication of machinery and equipment for various industries, ensuring the structural integrity and longevity of these systems.
- Electronics and Electrical Components: In the electronics and electrical industries, butt welding is used to join conductive wires, cables, and components, ensuring efficient electrical connections.
- Medical Devices: Butt welding is utilized in the manufacturing of medical devices and instruments, where precision, cleanliness, and biocompatibility are essential.
- Food and Beverage Industry: Butt welding is employed in the construction of stainless steel equipment and pipelines used in food and beverage processing, ensuring hygiene and corrosion resistance.
- Nuclear Industry: Butt welding is used in the fabrication of components for nuclear reactors and related infrastructure, where the integrity of welds is critical for safety.
- Environmental Engineering: Butt welding is used in the construction of wastewater treatment plants, water distribution systems, and environmental containment structures.
These are just a few examples of the diverse applications of butt welding across industries. Its ability to create strong, durable, and reliable joints makes it a preferred choice for many critical welding tasks. However, the specific techniques and equipment used may vary depending on the industry and the materials being joined.
Advantages of Butt Welding
Butt welding is a welding technique that joins two pieces of metal together at their ends, creating a strong and durable connection. There are several advantages to using butt welding:
- Strong and Durable Joints: Butt welding creates a weld joint that is as strong as or even stronger than the base materials being joined. This results in a reliable and long-lasting connection.
- Minimal Material Waste: Butt welding minimizes material waste since it requires only the ends of the workpieces to be prepared for welding. This is particularly advantageous when working with expensive or scarce materials.
- Clean and Aesthetically Pleasing: Butt welds produce clean and smooth joints, making them suitable for applications where aesthetics matter, such as architectural structures and automotive components.
- No Filler Material Needed (in some cases): In certain cases, butt welding can be performed without the need for additional filler material, which can reduce costs and complexity.
- Versatility: Butt welding can be used to join a wide range of materials, including metals and plastics. It is applicable to various industries, including manufacturing, construction, and aerospace.
- High Efficiency: Butt welding is a fast and efficient welding process, which can help save time and labor costs in production.
- Uniform Strength: The resulting weld joint typically has uniform strength along its entire length, ensuring consistent performance under stress or load.
- Minimal Distortion: Butt welding typically results in minimal distortion of the workpieces, which is important for applications where precise dimensions are critical.
- Reduced Heat-Affected Zone (HAZ): Compared to some other welding methods, butt welding can produce a smaller heat-affected zone, reducing the likelihood of material weakening or distortion.
- Weld Quality Control: Butt welding can be easily monitored and controlled to ensure the quality of the weld, making it suitable for critical applications.
- Automation Compatibility: Butt welding is amenable to automation, which can further increase efficiency and reduce human error in manufacturing processes.
- Environmental Benefits: The minimal material waste and efficient use of resources in butt welding contribute to its eco-friendliness compared to some other joining methods.
It’s worth noting that while butt welding offers numerous advantages, it may not be suitable for all welding applications. Factors such as material type, thickness, and joint configuration should be considered when selecting the appropriate welding method. Additionally, proper training and equipment are essential for achieving high-quality butt welds.
Disadvantages of Butt Welding
While butt welding offers several advantages, it also has certain disadvantages and limitations:
- Limited Joint Types: Butt welding is primarily used for joining two pieces of metal at their ends, making it less versatile for complex joint configurations compared to other welding techniques like fillet welding.
- Edge Preparation: Preparing the edges of the workpieces for butt welding can be time-consuming, especially for thicker materials. Proper edge preparation is essential for achieving high-quality welds.
- Material Thickness Limitations: Butt welding is more suitable for thinner to moderately thick materials. It may not be practical or cost-effective for extremely thick materials.
- Welding Equipment: Butt welding often requires specialized equipment such as butt welding machines, which can be expensive and require maintenance.
- Skill and Training: Achieving high-quality butt welds requires skilled operators who are trained in the technique. Inexperienced welders may struggle to produce consistent and reliable welds.
- Heat Input: Butt welding generates a significant amount of heat, which can lead to distortion, warping, or material weakening in some cases. Proper heat management is crucial to mitigate these issues.
- Limited Accessibility: Butt welding may not be feasible in situations where the ends of the workpieces are difficult to access, such as in tight corners or confined spaces.
- Noxious Fumes and Radiation: Like other welding processes, butt welding produces fumes and potentially harmful radiation. Adequate ventilation and protective measures are necessary to ensure the safety of the welder and others in the vicinity.
- Weld Quality Inspection: Ensuring the quality of butt welds can be challenging, and defects may not always be visible to the naked eye. Non-destructive testing methods may be required to detect hidden flaws.
- Not Suitable for All Materials: Butt welding is primarily used for metals and some plastics. It may not be suitable for materials with significantly different melting points or properties.
- Limited Portability: The equipment used in butt welding is often stationary and not easily portable, which can limit its application in certain situations.
- Welding Costs: While butt welding can be efficient, the initial investment in equipment and the need for skilled operators can make it costlier than some other welding methods for small-scale projects.
- Surface Finish: Butt welds may require additional finishing to achieve a smooth and aesthetically pleasing surface, which can add time and cost to the welding process.
Despite these disadvantages, butt welding remains a widely used and effective welding technique, especially for applications where strength, durability, and precision are paramount. Proper training, equipment selection, and process control can help mitigate many of the drawbacks associated with butt welding.
Check Out Other Important Topics
| IC Engine | Important PDFs | Boilers | Synergy Maritime Exam | Naval Arch | MEO Class 4 |
| Interview Questions | Difference Between | Types of Pumps | Auxiliary Machines | Types of Valves | Home |


