Single plate clutch :- In This article, we are going to discuss What is Single Plate Clutch ? It’s Diagram, Working Principle, Constructions, Applications, Advantages and Disadvantages With Simple Diagram for Better Understanding.
What is Single Plate clutch ?
A single plate clutch is a type of mechanical device used in vehicles with manual transmissions to connect and disconnect the power flow between the engine and the transmission. It consists of a single friction plate, known as the clutch plate or friction disc, which is placed between the engine’s flywheel and the pressure plate. When the clutch is engaged, the pressure plate applies force to the clutch plate, causing it to grip the flywheel tightly and transmit power from the engine to the transmission. This allows the vehicle to move forward or backward.
On the other hand, when the clutch is disengaged, the pressure plate releases its clamping force, causing the clutch plate to separate from the flywheel. This interrupts the power transfer, allowing the driver to change gears or bring the vehicle to a stop without stalling the engine. The clutch pedal is used by the driver to control the engagement and disengagement of the clutch.
Single plate clutches are widely used due to their compact design, lightweight nature, and smooth engagement characteristics. They are commonly found in passenger cars, motorcycles, and light commercial vehicles. However, in applications that require higher torque capacity or heavy-duty usage, multi-plate clutches may be preferred.
Read more :- Multi plate clutch
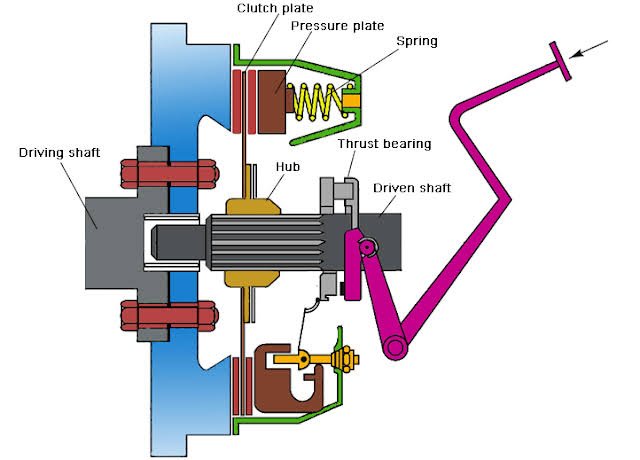
Single plate clutch diagram

construction and working of single plate clutch
The components of a single plate clutch are arranged systematically to ensure its proper operation. The clutch itself is the most crucial part, consisting of a plate with friction lining on both sides.
In addition to the clutch plate, there are several other components that contribute to the effective functioning of the clutch. These include the flywheel, pressure plate, thrust bearings, hubs, springs, and mechanisms for engaging and disengaging the clutch.
The clutch plate moves in an axial direction along the driven shaft and is connected to the hub positioned between the flywheel and the pressure plate. The clutch plate must have a single plate design, with friction lining on both sides, as it sits between the flywheel and the pressure plate.
The transmission of power in the single-plate clutch is facilitated by the friction torque. The pressure plate, connected to the flywheel and equipped with springs, plays a crucial role in enabling the movement of the clutch plate towards the flywheel.
A lever, along with a mechanism on the driven shaft, is attached to the thrust bearings. These bearings transmit the input and output speeds from the clutch pedal.
By reorganising the various components in a systematic manner, a single plate clutch ensures efficient power transmission and enables smooth engagement and disengagement of the clutch mechanism.
Parts of single plate clutch
The construction of a single plate clutch involves several key components:

- Clutch Plate/Friction Disc: The clutch plate, also known as the friction disc, is a circular disc made of a high-friction material such as organic or ceramic material. It is connected to the splined hub and is sandwiched between the flywheel and the pressure plate. The friction disc provides the necessary grip to transmit power between the engine and the transmission.
- Flywheel: The flywheel is a heavy, circular-shaped component bolted to the rear of the engine’s crankshaft. It acts as a rotating mass and provides inertia to smoothen out engine fluctuations. The clutch plate is in direct contact with the flywheel and transfers power to it.
- Pressure Plate: The pressure plate is a flat, circular-shaped component positioned adjacent to the flywheel. It is responsible for applying clamping force to the clutch plate against the flywheel. The pressure plate consists of a cover assembly and a diaphragm spring or a set of coil springs. The springs exert pressure on the clutch plate to maintain contact and transfer power.
- Release Bearing/Throw-out Bearing: The release bearing, also known as the throw-out bearing, is a small bearing positioned at the center of the pressure plate. It is responsible for transmitting the force from the clutch pedal to the pressure plate. When the clutch pedal is pressed, the release bearing disengages the pressure plate from the clutch plate, allowing for gear changes or disengagement of power.
- Clutch Housing: The clutch housing is a metal casing that encloses the clutch components. It provides support and protection to the clutch assembly and is usually bolted directly to the engine block or the transmission housing.
- Clutch Fork and Release Mechanism: The clutch fork is a lever connected to the release bearing. It is actuated by the clutch pedal through a series of linkages and cables or a hydraulic system. When the clutch pedal is pressed, the clutch fork moves the release bearing against the pressure plate, releasing the clamping force and disengaging the clutch.
These components work together to facilitate the engagement and disengagement of power between the engine and the transmission, allowing for smooth gear shifts and control over the vehicle’s movement.
working principle of single plate clutch
A single plate clutch operates based on the principle of friction. It utilizes the frictional force between two surfaces to transfer power from the engine to the transmission.
When the clutch is engaged, the clutch plate is pressed against the flywheel by the clamping force of the pressure plate. This creates a frictional connection between the clutch plate and the flywheel. As the engine rotates, the friction between these surfaces allows the clutch plate to rotate along with the flywheel, transmitting power to the transmission input shaft.
When the clutch is disengaged, the clamping force on the clutch plate is released, separating it from the flywheel. This interrupts the frictional connection and prevents power transmission. In this state, the engine can run independently without transferring power to the transmission, allowing for gear changes or the vehicle to remain stationary.
The principle of friction is essential for the proper functioning of the single plate clutch. The friction material on the clutch plate provides the necessary grip to transmit power, while the pressure plate ensures sufficient clamping force to maintain the frictional connection.
Single Plate Clutch working :
The working of a single plate clutch involves the following steps:
- Engaged Position: When the clutch pedal is not pressed, the clutch is in the engaged position. In this state, the clutch plate is pressed against the flywheel by the clamping force of the pressure plate. The friction between the clutch plate and the flywheel allows the transmission of power from the engine to the transmission input shaft. This enables the vehicle to move.
- Disengagement: When the driver presses the clutch pedal, it actuates the release mechanism. The release bearing pushes against the diaphragm spring or the pressure plate fingers, causing them to move backward. This action releases the clamping force on the clutch plate, separating it from the flywheel. As a result, the power transmission between the engine and the transmission is interrupted.
- Gear Shifting: With the clutch disengaged, the driver can now shift gears. The disconnected state between the engine and the transmission allows for smooth gear changes without causing damage to the transmission or stalling the engine. The driver can select the desired gear using the gear lever or shift mechanism.
- Engaging the Clutch: Once the desired gear is selected, the driver gradually releases the clutch pedal. As the pedal is released, the release mechanism allows the pressure plate to move forward, reapplying the clamping force on the clutch plate. The clutch plate engages with the rotating flywheel, resuming the power transmission between the engine and the transmission.
- Power Transfer: As the clutch plate engages with the flywheel, the friction between them allows the power from the engine to be transmitted to the transmission. This enables the vehicle to move forward or backward, depending on the selected gear.
The process of engaging and disengaging the clutch allows the driver to smoothly control the power flow between the engine and the transmission, facilitating gear changes and proper vehicle operation. It is essential to master the coordination between the clutch pedal and the accelerator to ensure smooth shifting and efficient driving.
Application of single plate clutch
Single plate clutches have various applications in different vehicles and machinery. Here are some common applications of single plate clutches:
- Automobiles: Single plate clutches are extensively used in passenger cars, motorcycles, and light commercial vehicles with manual transmissions. They allow smooth engagement and disengagement of power between the engine and the transmission, enabling the driver to shift gears and control the vehicle’s speed.
- Industrial Machinery: Single plate clutches are employed in various industrial machinery, such as agricultural equipment, construction machinery, and power transmission systems. They are used to connect and disconnect power between the engine or motor and the driven component, allowing for controlled operation and efficient power transmission.
- Generators: Single plate clutches can be found in generators and power generation systems. They enable the engine to be disengaged from the generator when it is not needed, reducing fuel consumption and wear on the engine components.
- Pumps and Compressors: Single plate clutches are utilized in pumps and compressors to control the operation of the driven equipment. They allow for smooth start-up and shutdown of these devices, protecting the motor or engine from excessive stress and extending their lifespan.
- Marine Applications: Single plate clutches are commonly used in marine propulsion systems, including boats and ships. They facilitate the engagement and disengagement of the engine power to the propeller, enabling the vessel to maneuver, change speed, or stop as required.
Overall, single plate clutches are versatile components found in various mechanical systems, where they provide reliable power transmission and efficient control over the engagement and disengagement of the driving and driven components.
advantages of single plate clutch
Single plate clutches offer several advantages, including:
- Compact and Lightweight: Single plate clutches have a simple design and occupy less space, making them ideal for vehicles with limited engine compartment space. Their lightweight construction helps reduce the overall weight of the vehicle, contributing to improved fuel efficiency and performance.
- Smooth Engagement: Single plate clutches provide smooth engagement, allowing for seamless gear shifts. The friction material on the clutch plate ensures a gradual transfer of power, resulting in a comfortable driving experience without jerks or sudden jolts.
- Cost-Effective: Single plate clutches are generally more cost-effective compared to other clutch types, such as multi-plate clutches. Their simpler construction and fewer components make them easier to manufacture, maintain, and repair, resulting in lower costs for vehicle owners.
- Durability and Reliability: Single plate clutches are known for their durability and reliability. They can withstand regular usage and provide consistent performance over time, making them suitable for everyday driving conditions.
- Ease of Use: Single plate clutches are user-friendly and easy to operate. The clutch pedal effort required for engagement and disengagement is typically moderate, allowing for comfortable and effortless control by the driver.
- Wide Application Range: Single plate clutches are versatile and widely used in various types of vehicles, including passenger cars, motorcycles, and light commercial vehicles. They can handle a wide range of engine sizes and torque outputs, making them suitable for a variety of applications.
- Maintenance and Repair: Single plate clutches are relatively straightforward to maintain and repair. The clutch plate can be easily replaced when worn out, and the components are readily available in the market, contributing to cost-effective maintenance and shorter downtime during repairs.
Overall, the advantages of single plate clutches include their compact size, smooth engagement, cost-effectiveness, durability, ease of use, wide applicability, and simplified maintenance and repair procedures. These qualities make them a popular choice for vehicles with manual transmissions.
disadvantages of single plate clutch
While single plate clutches have several advantages, they also have a few disadvantages to consider:
- Limited Torque Capacity: Compared to multi-plate clutches, single plate clutches have a relatively lower torque capacity. This means they may not be suitable for high-performance vehicles or applications that require handling high levels of torque. In such cases, multi-plate clutches are preferred for their increased torque capacity and durability.
- Heat Dissipation: Single plate clutches can generate a significant amount of heat during operation, especially in situations where they are subjected to heavy loads or frequent engagement and disengagement. If the heat is not dissipated adequately, it can lead to clutch slippage, reduced performance, and accelerated wear of clutch components.
- Wear and Tear: The friction material on the clutch plate undergoes wear and tear over time, especially with repeated engagement and disengagement. This can lead to reduced clutch performance and the need for periodic replacement or maintenance.
- Clutch Slippage: In certain conditions, such as high engine torque or aggressive driving, single plate clutches may experience clutch slippage. Clutch slippage occurs when the clutch plate fails to maintain a sufficient grip on the flywheel, resulting in power loss and decreased acceleration.
- Limited Application Range: While single plate clutches are suitable for many vehicles and applications, they may not be the best choice for specialized or heavy-duty applications. Vehicles or machinery that require extreme torque handling, such as high-performance sports cars or heavy-duty industrial equipment, may require the use of multi-plate clutches for better performance and durability.
It is important to consider these disadvantages in relation to the specific requirements of the vehicle or machinery in order to determine the most appropriate clutch type for optimal performance and longevity.
difference between single plate clutch and multi plate clutch
| Feature | Single Plate Clutch | Multi-Plate Clutch |
|---|---|---|
| Design | Consists of a single clutch plate | Consists of multiple clutch plates |
| Friction Material | Single friction material on the clutch plate | Multiple friction materials on each clutch plate |
| Torque Capacity | Relatively lower torque capacity | Higher torque capacity |
| Application | Suitable for regular passenger cars, motorcycles, and light commercial vehicles | Preferred for high-performance vehicles, heavy-duty applications |
| Size and Weight | Compact and lightweight | Bulkier and heavier |
| Engagement | Smooth engagement | More aggressive engagement |
| Heat Dissipation | May generate more heat | Better heat dissipation |
| Cost | Generally more cost-effective | Often more expensive |
| Maintenance | Relatively easier to maintain and repair | May require more frequent maintenance and specialized repair |
| Durability | Generally durable and reliable | Highly durable and long-lasting |




