CCAI
What is CCAI ?
CCAI is the ratio of the fuel which indicates ignition quality because ignition directly depends on the Aromatic Content in the fuel.
Or
The calculated carbon aromaticity index is an index of the ignition quality of residual fuel oil.
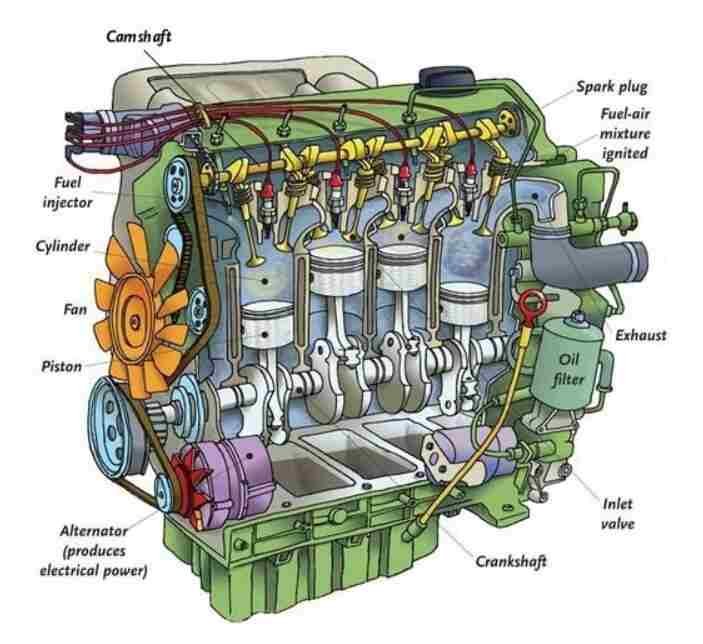
The operation of all internal combustion engines depends on the ignition quality of fuel.
For spark-ignition engines the fuel has an octane rating.
For the Diesel Engine ,it depends on the type of fuels.The cetane numbers are used for the distillate fuels.
Two other empirical indices are used for the residual fuel oil: CCAI and Calculated Ignition Index (CII).
Both CCAI and CII are calculated from the fuel density and kinematics Viscosity.
Formula for CCAI:
D= density at 15°C (kg/m3)
V= viscosity (cST)
t = viscosity temperature (°C)
Use
Normally, this will give a value somewhere between 800 and 880. The lower the value, the better the quality of the ignition. Fuels with a Calculated Carbon Aromaticity Index higher than 880 are often problematic or even unusable in diesel engines.
A Low Calculated Carbon Aromaticity Index Rating means better Ignition,Better fuel quality and less Ignition Delay.
Low Ratings are up to a Calculated Carbon Aromaticity Index ratio of 850
Range :- 850-950 ;870 be the limit for use.
Medium speed engine – < 840
For Slow speed engine – < 870
Aromatics –Benzene ring structures present in the fuel which affect the ease of which a hydrocarbon fuel molecules can burn.
Full form :-
Calculated Carbon Aromaticity Index