what is dog clutch?
A dog clutch, also known as a dog gear or dog-tooth clutch, is a type of mechanical clutch establishes a connection between two rotating shafts or other rotating components through the engagement of interlocking teeth or dogs. It is designed to engage and disengage two rotating shafts or components quickly and securely. The clutch gets its name from the dog-like teeth or projections on its surface.
The dog clutch consists of two components: a driving member and a driven member. These members have mating teeth or projections that interlock when engaged and separate when disengaged. The teeth or projections are typically rectangular or square in shape, resembling the teeth of a dog.
To engage the dog clutch, the driving member and driven member are brought into contact, and the teeth or projections of one member mesh with the corresponding spaces or recesses on the other member. This interlocking engagement allows torque and rotational motion to be transmitted from the driving member to the driven member.
Disengaging the dog clutch involves separating the teeth or projections of the driving and driven members. This is typically done by moving the members apart or by using a mechanism that allows the teeth to disengage smoothly and quickly.
Dog clutches are commonly used in manual transmissions, gearboxes, and other mechanical systems where rapid engagement and disengagement of rotating components are required. They are valued for their simplicity, compact design, and ability to handle high torque loads. Dog clutches are often used in applications that require quick gear changes, such as in racing vehicles or high-performance machinery.
However, it is important to note that dog clutches can produce a noticeable “clunk” or noise when engaged due to the teeth or projections abruptly meshing. Proper design, lubrication, and synchronisation mechanisms are necessary to ensure smooth and reliable operation.
Must Read : Single Plate Clutch
dog clutch diagram

Construction of Dog Clutch
The construction of a dog clutch involves specific components that enable its functioning. Here is a simplified explanation of the typical construction of a dog clutch:
- Driving Member: The driving member of a dog clutch is usually connected to the source of power, such as an engine or motor. It contains the teeth or projections that engage with the driven member.
- Driven Member: The driven member of a dog clutch is connected to the component that receives power or motion from the driving member. It also has corresponding spaces or recesses that align with the teeth or projections of the driving member.
- Teeth or Projections: Both the driving and driven members have mating teeth or projections on their surfaces. These teeth or projections are typically rectangular or square in shape, resembling the teeth of a dog. The number, size, and arrangement of these teeth or projections can vary based on the specific design and application requirements.
- Engagement Mechanism: The engagement mechanism allows the teeth or projections of the driving member to interlock with the spaces or recesses of the driven member. This mechanism ensures that the teeth or projections align properly during engagement, creating a secure connection.
- Disengagement Mechanism: The disengagement mechanism facilitates the separation of the teeth or projections, allowing for the smooth and quick disengagement of the dog clutch. This mechanism enables the driving and driven members to move apart, separating the interlocked teeth or projections.
- Lubrication: Proper lubrication is essential for the smooth operation and longevity of the dog clutch. Lubricating the teeth or projections reduces friction, wear, and heat generation during engagement and disengagement.
- Housing or Casing: The dog clutch is usually housed within a protective casing or housing that provides support, protection, and proper alignment of the driving and driven members. The housing also contains mechanisms for adjusting and controlling the engagement and disengagement process.
The specific construction details of a dog clutch can vary depending on the design requirements, application, and load capacity. Advanced designs may incorporate additional features for improved performance, such as synchronisation mechanisms in manual transmissions. Proper design, materials, and manufacturing techniques ensure the durability and reliable operation of the dog clutch.
Working of Dog Clutch
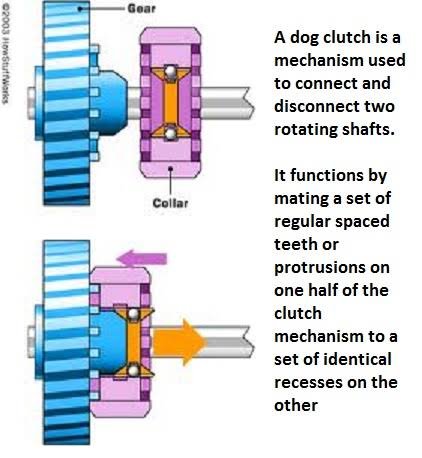
The working principle of a dog clutch involves the engagement and disengagement of two rotating components through interlocking teeth or projections, resembling the teeth of a dog. Here is a simplified explanation of how a dog clutch works:
- Components: It consists of two main components: a driving member and a driven member. These members have mating teeth or projections on their surfaces.
- Engagement: To engage the dog clutch, the teeth or projections of the driving member are aligned with the corresponding spaces or recesses on the driven member. When the two members are brought together, the teeth or projections interlock, creating a secure connection.
- Torque Transmission: Once engaged, torque and rotational motion can be transmitted from the driving member to the driven member. The interlocking teeth or projections ensure a positive and direct transfer of power.
- Disengagement: Disengaging the dog clutch involves separating the teeth or projections of the driving and driven members. This is typically achieved by moving the members apart or using a mechanism that allows the teeth to disengage smoothly and quickly.
- Rapid Operation: It is designed for quick engagement and disengagement. The teeth or projections are positioned in such a way that they can easily slide past each other during the engagement and disengagement process. This rapid operation allows for swift changes in rotational motion or gear shifting.
- Synchronization (in certain applications): In applications like manual transmissions, additional synchronization mechanisms are employed to ensure smooth gear shifting. Synchronization helps to match the rotational speeds of the engaging components, minimizing gear clash and ensuring a smooth transition.
- Load Capacity: It is capable of handling high torque loads due to the secure interlocking of the teeth or projections. This makes them suitable for applications where reliable and efficient torque transmission is required.
The working of a dog clutch relies on the interlocking teeth or projections to provide a positive and secure connection between the driving and driven members. This allows for rapid engagement and disengagement, making dog clutches ideal for applications where quick and reliable transmission of rotational motion is necessary.
applications of dog clutch
Dog clutches find applications in various industries and machinery where rapid engagement and disengagement of rotating components are required. Some common applications of dog clutches include:
- Manual Transmissions: It is widely used in manual transmissions of vehicles, such as cars, motorcycles, and racing vehicles. They enable smooth and quick gear changes by providing a reliable connection between the engine and the gearbox. The dog clutch allows the driver to engage or disengage different gears swiftly and efficiently.
- Gearboxes: It is employed in gearboxes used in machinery and equipment, including industrial machinery, agricultural machinery, and construction equipment. They facilitate gear shifting in these applications, enabling the transmission of torque and power between different gears or speed ranges.
- Power Tools: It is utilized in power tools like drills, grinders, and impact wrenches. They allow for the rapid engagement and disengagement of the rotating tool components, enabling efficient operation and quick tool changes.
- Printing Presses: It is incorporated into printing presses, especially those used for high-speed printing operations. They enable fast engagement and disengagement of the printing cylinders or plates, allowing for precise control over the printing process.
- Packaging Machinery: It is employed in packaging machinery, such as filling machines, labeling machines, and carton sealing machines. They assist in the quick and accurate movement of the packaging components, ensuring efficient packaging operations.
- Industrial Equipment: It find applications in various industrial equipment and machinery where rapid engagement and disengagement are required. This includes machine tools, conveyors, textile machinery, and more. Dog clutches allow for precise control over the rotational movements of these machines, enhancing productivity and operational efficiency.
It is important to note that the specific applications of dog clutches may vary depending on the design requirements, torque capacity, and the need for rapid and reliable engagement and disengagement. Dog clutches offer a robust and efficient solution for various mechanical systems that require quick and secure transmission of rotational motion.
advantages of dog clutch
Dog clutches offer several advantages in applications where rapid engagement and disengagement of rotating components are required. Some key advantages of dog clutches include:
- Quick and Reliable Engagement: It provide fast and reliable engagement of rotating components. The teeth or projections on the clutch allow for rapid connection, ensuring minimal time delay in transmitting torque and rotational motion.
- High Torque Capacity: It is capable of handling high torque loads. The interlocking teeth or projections provide a secure and robust connection, allowing for the efficient transfer of power between the driving and driven components.
- Compact Design: It has a compact design, making them suitable for applications where space is limited. The simplicity of their construction allows for easy integration into various mechanical systems and equipment.
- Cost-Effective: It is relatively simple in design and require fewer components compared to other types of clutches. This simplicity translates to lower manufacturing and maintenance costs, making dog clutches a cost-effective solution.
- Minimal Power Loss: It has a direct and positive engagement mechanism, resulting in minimal power loss during operation. This makes them efficient in transmitting torque and rotational motion without significant energy wastage.
- Durability and Longevity: The interlocking teeth or projections in dog clutches provide a sturdy and reliable connection. This results in a durable clutch mechanism that can withstand frequent engagement and disengagement cycles, ensuring a longer service life.
- Ease of Maintenance: It is relatively easy to maintain. Lubrication and periodic inspection of the teeth or projections are typically sufficient to ensure proper functioning. This ease of maintenance contributes to the overall reliability and longevity of the clutch.
- Versatile Applications: It find applications in a wide range of industries and machinery that require rapid engagement and disengagement. They are suitable for manual transmissions, gearboxes, power tools, printing presses, packaging machinery, and various industrial equipment.
Overall, the advantages of dog clutches lie in their quick and reliable engagement, high torque capacity, compact design, cost-effectiveness, minimal power loss, durability, ease of maintenance, and versatility. These advantages make dog clutches a preferred choice in applications where fast and secure transmission of rotational motion is crucial.
disadvantages of dog clutch
While dog clutches offer several advantages, there are also some disadvantages associated with their use. Here are some key disadvantages of dog clutches:
1.Noise and Vibration: It can produce noticeable noise and vibration during engagement and disengagement. The abrupt meshing of the teeth or projections can cause a clunking sound, which may be undesirable in certain applications.
2.Limited Engagement Options: It typically offer a limited number of engagement positions. They often provide a direct engagement between two components, which may not allow for intermediate or partial engagement positions. This limitation may restrict the versatility of the clutch in certain applications.
3.Synchronization Requirements: In some applications, such as manual transmissions, dog clutches require proper synchronization to ensure smooth gear shifting. Synchronization mechanisms or techniques are necessary to match the rotational speeds of the engaging components, preventing gear clash or damage during shifting.
4.Potential for Damage: If the engagement and disengagement of a dog clutch are not properly synchronized, or if excessive force is applied during engagement, it can result in damage to the teeth or projections. This can lead to premature wear, reduced clutch performance, or even clutch failure.
5.Wear and Maintenance: The teeth or projections of a dog clutch are subject to wear due to the repeated engagement and disengagement cycles. Regular inspection and maintenance of the clutch are necessary to ensure proper functioning and to address any wear-related issues.
6.Smoothness of Engagement: The engagement of a dog clutch can sometimes be less smooth compared to other types of clutches. The teeth or projections may cause slight jolts or jerks during engagement, which may be noticeable in certain applications or may require additional design considerations for achieving smoother operation.
7.Design Complexity for Multiple Gears: In applications requiring multiple gears, such as complex gearboxes, the design and arrangement of dog clutches can become more intricate. Achieving proper gear selection and synchronisation among multiple clutches may require additional engineering and design complexity.
It’s important to note that the disadvantages mentioned above are specific to dog clutches and may vary depending on the application and design considerations. Proper design, lubrication, synchronisation mechanisms, and maintenance practices can help mitigate some of these disadvantages and ensure the reliable operation of dog clutches.
Reference : https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Dog_clutch
What is a dog clutch?
A Dog Clutch is a mechanical device which us used to couple two rotating shafts by engagement of interlocking teeth.
Why is it called dog clutch?
In certain cases, including those found in automatic transmissions, there are clutches that can lock up by means of engaging dogs instead of relying solely on friction. These particular clutches are known as dog clutches, and the interlocking components within them are referred to as clutch dogs.

