Maintaining a safe atmosphere on ships is very important and Inert gas system on ships are fitted for the same reason. IG system on ship helps to maintain an inert atmosphere inside the cargo holds to avoid any explosion or accidents.
In order to understand the proper functioning on Inert Gas System, let’s clear out some basic terms which will be helpful in understanding the whole process.
What is Inert Gas ?
An Inert gas is a gas which does not take part in chemical reaction under a given set of conditions.
In simple language, Inert gas is the gas which contains insufficient oxygen ( Normally, less than 8 percent ) to prevent or avoid combustion of flammable gases.
What is IG System or Inert Gas System on Ship ?
An Inert Gas System installed on a tanker is designed to prevent explosion in a tanker’s cargo tank by maintaining a non-explosive atmosphere inside the tank by reducing the oxygen limit inside the space insufficient to cause explosion.
It is used for safe operation of ship so, Gas freeing must be carried out subsequently if workers have to enter the empty tanks.
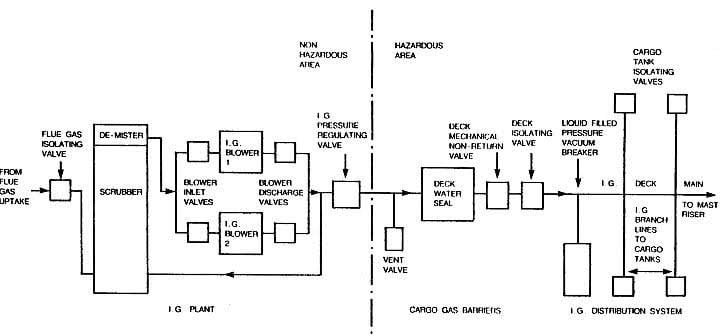
Inert Gas System Diagram
Image of I.G System
As we know that fire needs oxygen, heat, and fuel to burn. If we remove One of the elements of the fire triangle, we can prevent fire.
Principle of Inert Gas System on Ships
The basic principle of inert gas system is to remove the oxygen content by introducing inert Gas to any compartment that contains a mixture of hydrocarbon gases.
Thus, system minimize the risk of explosion.
The inert gas system delivers inert gas over the oil cargo hydrocarbon mixture, increasing the LEL lower explosion limit (lower concentration at which vapours can be ignited) while decreasing the higher explosion limit HEL (Higher concentration at which vapour explodes).
When the concentration reaches around 10%, an atmosphere inside the tank is created in which hydrocarbon vapours cannot burn. As a safety precaution, the concentration of inert gas is kept at around 5%.
What is The Purpose of The Inert Gas System on Ship ?
Oil tankers transport oil of various grades and quality, which has the ability to produce flammable vapours and gases when loaded for transportation. Even though there is no cargo on board, there may be dangerous flammable gases available in the hold.
When the vapour produced by an oil cargo is mixed with a specific concentration of air primarily containing oxygen, an explosion can occur, resulting in property damage, marine pollution, and loss of life.
Onboard, an inert gas system is used to protect against such explosions. A separate inert gas plant or flue gas produced by a ship’s boiler can be used. Inert gas systems are used for preventing the formation of flammable conditions inside spaces containing a flammable product, such as the vapour space of storage tanks.
Working of Inert Gas System
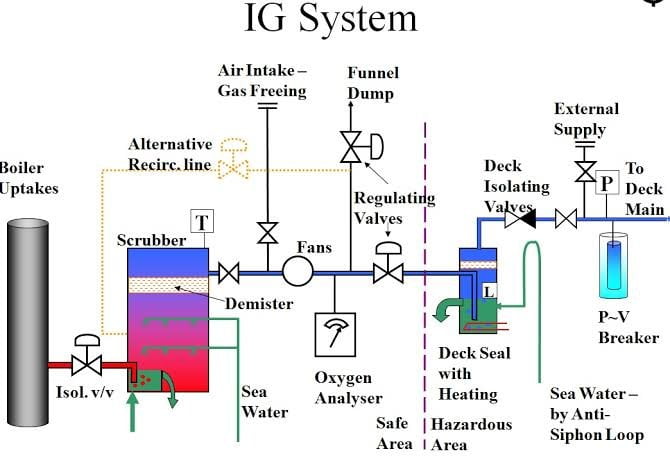
- Hot Flue gases from the exhaust of Boiler is taken to the bottom of the scrubber tower through the boiler uptake valve.
- In the scrubber tower, Flue gases are passes through a series of water spray and baffle plates to cool, clean, and moisten the gases. The SO2 level drops by up to 90% and the gas becomes soot-free.
- The flue gas come out from the scrubber tower is free from shoot and So2.
- But it contains moisture. So, it is then passed through a demister to remove moisture before leaving to suction of the blower.
- The treated gas is delivered to the tanks by motor-driven inert gas blowers from the scrubber tower. They are supported by rubber vibration absorbers and are separated from the piping by rubber expansion bellows.
- The gas control valves ( pressure regulating valve ) regulate the amount of gas delivered to the deck, and the pressure controller controls the deck pressure. If the deck pressure is lower than the set point, the output signal will be raised to increase the opening of the valve, and vice versa if the deck pressure is higher than the set point. These valves will then work together to maintain both the deck pressure and the blower pressure at their respective setpoints without starving or overfeeding the circuit.
- The gas passes through the deck water seal before entering the deck line, which also acts as a non-return valve, preventing the back-flow of explosive gases from the cargo tanks.
- After the deck seal, the inert gas relief is fitted to balance built-up deck water seal pressure when the system is shut down. In conditions of a failure of both the deck seal and the non-return valve, the relief valve did the work of venting the gases flowing from the cargo tank into the atmosphere.
- The oxygen analyzer is fitted after the blower. It separates the production and distribution components of the plant.
- It analyzes oxygen content in the gas and if it is more than 8 percent, alarms activated and shutdown the plant.
Inert Gas System Components with Description
1. Exhaust Gas Sources :- The source of Inert gas is a.) Exhaust Uptake of Boiler and b.) Exhaust Uptake of Main engine. It is because Exhaust gas contains flue gases in it.
2. Inert Gas Isolating Valve :- As the name suggest, it isolate the System from the exhaust uptake.
3. Scrubbing Tower :- The flue gas enters the scrubbing tower from the bottom and passes through a series of water spray and baffle plates to cool, clean, and moisten the gases. The SO2 level drops by up to 90% and the gas becomes soot-free.
4. Demister :- A demister is a device often fitted to vapor–liquid separator vessels to enhance the removal of liquid droplets entrained in a vapor stream.
Here, it is used for absorbing moisture and water from the treated flue gas. Generally, it is made up of polypropylene.
5. Gas Blower :- Typically, two types of fan blowers are used: a steam-driven turbine blower for I.G operation and an electrically driven blower for topping off.
6. I.G pressure Regulating valve :- The pressure within the tanks varies depending on the oil’s properties and the atmospheric conditions. To control this variation and prevent the blower fan from overheating, a pressure regulator valve is attached after blower discharge, re-circulating the excess gas back to the scrubbing tower.
7. Oxygen Analyzer: It is a device fitted after the pressure regulating valve. If the oxygen level is more than 8% by volume, it will sound an alarm and release inert gas to the atmosphere.
8. Deck seal :- The deck seal’s purpose is to prevent gases from returning from the blower to the cargo tanks. Generally, Deck seals of the wet type are used. To absorb the moisture carried away by the gases, a demister is installed.
9. Mechanical Non return valve :- It is an additional non-return mechanical device in line with the deck seal.
10. Deck Isolating Valve : – This Valve is used for Isolating engine room system Fully with deck system.
11. Pressure Vacuum breaker :- The PV breaker valve used for controlling the over or under pressurization of the cargo tank. The PV breaker vent is equipped with a flame trap to prevent a fire from igniting while in port during loading or discharging operations.
12. Cargo Tank Isolating Valve :- A vessel has a number of cargo holds, each of which has an isolating valve. The valve regulates the flow of inert gas to hold and is only operated by a responsible officer on board.
13. Mast Riser :- Mast riser is used for maintaining a positive pressure of inert gas at the time of loading of cargo and during the loading time it is kept open to avoid pressurization of the cargo tank.
14. Safety and Alarm Systems :- The Inert gas system is fitted with safety and alarm system for safe operation of ship.
Alarms and Systems Fitted in IG System
A. A high level in the scrubber raises an alarm, allowing the blower and scrubber tower to shut down.
B. Low-pressure seawater supply to the scrubber tower (approximately 0.7 bar) causes an alarm and shutting down of blower.
C. A low pressure seawater supply (approximately 1.5 bar) to the deck seal causes an alarm and the blower to shut down.
D. High inert gas temperature (approximately 70 degrees Celsius) causes an alarm and the blower to shut down.
E. Low pressure in the line after the blower (approximately 250mm wg) causes an alarm and the blower to shut down.
F. A high oxygen content (8%) causes an alarm and the shutdown of gas delivery to the deck.
G. A low level in the deck seal causes an alarm and the gas supply to the deck to be cut off.
H. Power failure leads to alarm and shutdown of blower and scrubber tower
I. An emergency stop causes an alarm and the blower and scrubber tower to shut down.
The various alarms incorporated in the Inert Gas plant are following :-
A. Scrubber low level
B. Deck seal High level
C. Low O2 Content (1%)
D. High O2 Content (5%)
E. Low lube oil pressure alarm
Inert Gas System Starting Procedure
Onboard, careful consideration is required for the inert gas system to function properly. The oxygen content must always be kept at 5% by volume; any further reduction in oxygen content will result in the mixing of impurities in the gas, which will be difficult to separate. Before starting the inert gas system, certain precautions must be taken.
1. Open the valve related to the burner of fuel and check Fuel is adequate or not for operation of Boiler and Inert gas generator.
2. Switch on the electric power of Control panel.
3. The scrubber’s water drain lines must be opened.
4. Check and ensure that the oxygen analyzer is working properly and required then calibrate.
5. Set pressure control setting for inert gas in distribution lines.
6. Set the pressure control valve of the burner.
7. Ensure supply of sea water to the deck seal.
8. Check and ensure that The system lines are lined up.
9. Before entering the port, start the inert gas generator. (Actually, this is done to avoid dark black smokes from coming out when it starts.)
Inert Gas System Starting Procedure
1. Follow all the I.G system checklist as per guidelines of company.
2. Check and ensure that all cargo openings are closed.
3. Prior to start, line up the system properly.
4. Take the precautionary measure mentioned above.
5. Start the IG system
6. Check the oxygen analyser readings.
7. Supply inert gas to the Deck opening Inert gas main supply valve.
8. Keep an eye to the all Pressure parameters.
9. During cargo Operations, Monitor the temperature and the oxygen level of inert gas.
10. Increase the pressure of inert gas before stopping the inert gas plant.
Also Read : Steering Gear
Oily Water Separator on Ships
Fresh Water Generator
Centrifugal Pump Parts Working Diagram
Heat Exchanger Types Working Principle
What is the purpose of inert gas?
Inert gases are commonly used to prevent unwanted chemical reactions from degrading a sample. These unfavourable chemical reactions are frequently oxidation and hydrolysis reactions with air’s oxygen and moisture.
Inert gases are also used to remove oxygen from confined spaces where combustible gases are present, such as certain sewers.
Which inert gas systems use only gases from the ship’s main or auxiliary boiler?
The flue gas plant.
How is the inert gas fed into cargo tanks?
Process used for Inerting is Displacement Method.
The displacement method differs slightly from the dilution method. The inert gas is used to displace the air inside the tank in this method. With this method, close to one air change is required to achieve less than 8% oxygen from an initial 21%.
What are the 7 inert gases?
1. Helium (He)
2. Neon (Ne)
3. Argon (Ar)
4. Krypton (Kr)
5. Xenon (Xe)
6. Radon (Rn)
7. Oganesson (Og)
Check Out Other Important Topics
| IC Engine | Important PDFs | Boilers | Synergy Maritime Exam | Naval Arch | MEO Class 4 |
| Interview Questions | Difference Between | Types of Pumps | Auxiliary Machines | Types of Valves | Home |