Centrifugal Clutch Working Principle ,Parts, Constructions, applications, advantages and disadvantages : In this article, we will delve into the functionality and operation of a centrifugal clutches, providing a comprehensive understanding of its purpose and mechanics.
What is Centrifugal clutch ?
A centrifugal clutch is a mechanical device that allows for the automatic engagement and disengagement of power transmission between a prime mover, typically an engine, and a driven component or load.
It operates based on the principle of centrifugal force, that’ why its name Centrifugal clutches. These are commonly used in various applications where controlled power transmission and ease of operation are essential.
The primary function of a centrifugal clutch is to enable power transmission from the prime mover to the driven component in a gradual and controlled manner. It achieves this through a combination of mechanical components and the principle of centrifugal force.
Must Read : Centrifugal Pump
Working principle of Centrifugal clutch
A Centrifugal clutch works on the principle of centrifugal Force allows for the automatic engagement and disengagement of power transmission.
Magnitude of centrifugal force increases along with increase of of speed and vice versa.
Working of centrifugal clutch ?
A centrifugal clutch is a mechanical device that engages and disengages power transmission between a driving shaft and a driven shaft. It operates based on the principle of centrifugal force.
The working principle of a centrifugal clutch involves the use of rotating weights or shoes that respond to changes in rotational speed. Here’s how it works:
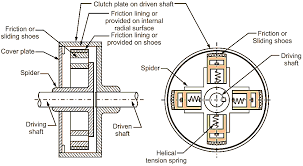
- Components: A centrifugal clutch consists of several key components, including a driving shaft, driven shaft, clutch drum, clutch shoes or weights, and springs.
- Mounting: The clutch drum is connected to the driving shaft, while the clutch shoes or weights are connected to the driven shaft. The shoes or weights are typically mounted on pivoting arms.
- Initial state: When the engine is at idle or the rotational speed is low, the clutch shoes or weights are in their relaxed or extended position. In this state, they do not make contact with the clutch drum.
- Increasing speed: As the rotational speed of the driving shaft increases, the clutch shoes or weights start to experience centrifugal force. This force causes them to move outward, towards the clutch drum.
- Engagement: When the centrifugal force becomes strong enough, the clutch shoes or weights overcome the resistance of the springs and make contact with the clutch drum. This engagement creates a solid connection between the driving shaft and the driven shaft.
- Power transmission: Once engaged, the clutch drum and the driven shaft rotate together, transferring power from the driving shaft to the driven shaft.
- Disengagement: When the engine speed decreases, the centrifugal force acting on the clutch shoes or weights reduces. The springs then push the shoes or weights back towards the center, away from the clutch drum.
- Decoupling: As the shoes or weights retract, they lose contact with the clutch drum, resulting in the disengagement of the clutch. This interrupts power transmission between the driving and driven shafts.
The centrifugal clutch’s working principle allows it to automatically engage and disengage based on the rotational speed of the driving shaft. It is commonly used in applications such as lawn mowers, go-karts, chainsaws, and other small engine-powered devices.
Parts of a Centrifugal clutch
These are the Parts of a Centrifugal Clutch:
- Drum
- Clutch basket
- Clutch plates
- Springs
- Shoe
- Friction lining
- Spider
- Weights
- Key
# Drum
A drum is an exterior portion of the clutch that revolves in tandem with the engine’s crankshaft. The drum contains all of the clutch’s components, including the guides, sliding shoes, springs, friction lining, and others. The driven shaft of the belt, chain, or transmission system connects to the drum.
The primary function of the drum in a centrifugal clutch is to provide a rotating surface for the engagement and disengagement of the clutch shoes.
#clutch basket
As the name suggests, the clutch basket is a stationary part of the clutch system that holds clutch plates until they are needed.
# clutch plates
In a centrifugal clutch, the clutch plate is an integral part of the clutch assembly. It works in conjunction with the clutch basket and other components to facilitate the engagement and disengagement of the clutch.
The clutch plate in a centrifugal clutch is typically a circular, disc-shaped component made of friction material. It is located inside the clutch basket and is in direct contact with the clutch shoes. The clutch plate is designed to provide the necessary friction to transmit power from the engine to the driven equipment.
# Spring
A clutch spring holds the clutch plate in place and helps keep the clutch plates engaged with each other. Spring is most commonly employed at slower speeds. Each shoe contains a spring.
The spring in a centrifugal clutch is a vital component that assists in the operation of the clutch assembly. It is responsible for controlling the engagement and disengagement of the clutch shoes, allowing the transfer of power from the engine to the driven equipment.
In a centrifugal clutch, there are typically multiple springs positioned between the clutch shoes and the clutch basket. These springs are designed to exert a specific amount of force or tension on the clutch shoes, influencing their movement and engagement.
# Shoe
The shoe in a centrifugal clutch is a key component responsible for transmitting power from the engine to the driven equipment. It works in conjunction with other components, such as the clutch basket, clutch plate, and springs, to facilitate the engagement and disengagement of the clutch.
In a centrifugal clutch, there are typically multiple shoes positioned around the inner circumference of the clutch basket. These shoes are usually made of metal or other friction material and are designed to interact with the clutch plate.
When the engine is idling or running at low speeds, the shoes are in a relaxed or disengaged position. As the engine speed increases, the centrifugal force acting on the shoes also increases. This force causes the shoes to move outward, making contact with the clutch plate.
When the shoes make contact with the clutch plate, friction is generated, allowing power to be transmitted from the engine to the driven equipment. This engagement occurs automatically as the engine speed rises, without the need for manual intervention.
# Friction Lining
The friction lining in a centrifugal clutch is a critical element that provides the necessary grip and friction for the clutch shoes to engage with the clutch plate. It is a specific type of material applied to the surface of the clutch shoes.
The friction lining is typically made of a high-friction material such as cork, Kevlar, or other composite materials. It is designed to withstand the heat, pressure, and wear generated during clutch engagement and disengagement.
The purpose of the friction lining is to create a strong grip between the clutch shoes and the clutch plate when the clutch engages. When the engine speed increases, the centrifugal force pushes the clutch shoes outward, causing the friction lining to make contact with the clutch plate. The friction generated between the lining and the plate allows power to be transferred from the engine to the driven equipment.
# Spider
It is a central part of the clutch assembly and is responsible for connecting the clutch shoes to the engine’s output shaft.
The spider in a centrifugal clutch is typically a star-shaped or spider-shaped hub with arms extending outward. Each arm of the spider is connected to a clutch shoe. The spider is mounted on the engine’s output shaft and rotates with it.
When the engine is idling or running at low speeds, the spider remains stationary, and the clutch shoes are in a relaxed or disengaged position. As the engine speed increases, the centrifugal force acting on the clutch shoes causes them to move outward. The arms of the spider pivot, allowing the shoes to make contact with the clutch plate.
The spider transfers the centrifugal force from the clutch shoes to the clutch plate, enabling the engagement of the clutch. It serves as a linkage between the engine’s output shaft and the clutch shoes, facilitating the power transmission.
# Weight
Weights, which are pieces attached to the drum, engage the clutch. As the engine speed rises owing to centrifugal force, the weights slide outward and make contact with the clutch basket, engaging the clutch.
# Key
the key is a small, rectangular metal piece that serves as a connection between the clutch hub or drum and the engine’s output shaft. It plays a crucial role in ensuring the proper alignment and secure attachment of the clutch assembly to the engine.
advantages of centrifugal clutch
The advantages of centrifugal clutch are ;
- Increased Efficiency:
One of the primary advantages of centrifugal clutches is their ability to improve overall system efficiency. By engaging and disengaging at specific engine speeds, these clutches allow the prime mover, such as an engine, to operate within its optimal speed range. This ensures that power is transferred when it is most efficient, reducing energy wastage and improving fuel economy. The result is a more sustainable and cost-effective operation, particularly in applications where power demands vary.
- Smooth Power Transmission:
Centrifugal clutches enable smooth and gradual power transmission from the prime mover to the driven component or load. Unlike traditional clutches that engage abruptly, centrifugal clutches engage progressively as the engine speed increases. This gradual engagement minimizes sudden jolts and vibrations, reducing wear and tear on both the clutch and the connected components. The result is a smoother operation, improved user comfort, and extended equipment lifespan.
- Load Protection:
Centrifugal clutches provide an added layer of protection to the system by automatically disengaging when the driven component encounters excessive loads or stalls. In such situations, the clutch senses the drop in engine speed and disengages, preventing damage to the system. This protective feature helps to avoid costly repairs and downtime, especially in applications where sudden overloads or unexpected stops are common, such as in industrial machinery or recreational vehicles.
- User-Friendly Operation:
Centrifugal clutches offer user-friendly operation, particularly in applications where manual clutch engagement would be impractical or inconvenient. For example, in small vehicles like scooters or minibikes, centrifugal clutches allow for easy acceleration without the need to manually operate the clutch. This simplifies the driving experience and makes these vehicles accessible to a wider range of users, including those with limited experience or physical capabilities.
- Maintenance Efficiency:
Another advantage of centrifugal clutches is their relatively low maintenance requirements. Compared to other types of clutches, such as friction clutches, centrifugal clutches have fewer wear parts and do not require regular adjustments or lubrication. This results in reduced maintenance costs and downtime for maintenance activities, making them an attractive choice for applications where minimal maintenance is desired.
- Versatile Applications:
Centrifugal clutches find applications across various industries and systems, showcasing their versatility. From automotive and industrial machinery to lawn and garden equipment and recreational vehicles, these clutches can be tailored to meet specific power transmission needs. Their adaptability to different torque and speed requirements makes them suitable for a wide range of applications, providing flexibility and efficiency to various systems.
disadvantages of centrifugal clutch
- Limited Control:
One of the main disadvantages of centrifugal clutches is the limited control they provide over the engagement and disengagement process. Unlike manual clutches that allow for precise control by the operator, centrifugal clutches rely on engine speed to determine when to engage or disengage. This lack of control can be a disadvantage in situations where fine-tuned power transmission is required, such as in high-performance vehicles or applications with varying load conditions.
- Slippage:
Centrifugal clutches may experience slippage during operation, particularly when subjected to high loads or sudden changes in engine speed. Slippage can result in power loss and decreased efficiency, as some of the engine’s power is not effectively transferred to the driven component. This can be a significant drawback in applications where maximum power transmission is critical, potentially affecting overall system performance.
- Heat Generation:
During prolonged or heavy-duty operation, centrifugal clutches can generate heat due to friction between the clutch components. Excessive heat buildup can lead to reduced clutch performance, increased wear, and even potential damage to the clutch assembly. It may be necessary to incorporate cooling mechanisms or consider alternative clutch types in applications where heat dissipation is a concern.
- Size and Weight:
Centrifugal clutches can be relatively larger and heavier compared to other types of clutches. This can pose challenges in applications where space or weight restrictions are important factors. The larger size and weight may require design considerations and may not be suitable for compact or lightweight systems.
- Limited Torque Range:
Centrifugal clutches have a limited torque range within which they can effectively operate. If the torque requirements exceed the clutch’s capabilities, it may result in clutch slipping or failure to engage properly. This limitation restricts the use of centrifugal clutches in high-torque applications, where other types of clutches, such as friction clutches or hydraulic clutches, may be more suitable.
- Wear and Maintenance:
While centrifugal clutches generally require less maintenance compared to some other clutch types, they are still subject to wear over time. The engagement surfaces, such as the clutch shoes and drum, may wear out and require periodic replacement. This maintenance requirement should be considered in the overall cost and lifespan analysis of the clutch system.
Centrifugal gears have some disadvantages that should be considered when considering their applications in various industries. disadvantages are Limitations in control, the possibility of slippage, the production of heat, concerns about size and weight, a small range of torque, and the need for wear and upkeep are all things that need to be carefully considered in relation to the application and expected performance. Even though they have these problems, centrifugal clutches are still widely used and have important benefits in many industries and systems.
applications of centrifugal clutch
Centrifugal clutches are versatile mechanical machine that find application in a wide range of industries. Their ability to optimize power transmission and provide controlled engagement makes them indispensable in numerous systems. Some of the applications of centrifugal clutches, which are used in various industries.
- Automotive Industry:
The automotive industry extensively utilizes centrifugal clutches in vehicles such as scooters, minibikes, and go-karts etc. These clutches allow for the smooth acceleration and efficient power transfer from the engine to the drivetrain. By engaging at optimal engine speeds, it enhance fuel economy and deliver a comfortable driving experience. In automatic transmissions, they aid in seamless shifting, improving overall performance.
- Industrial Machinery:
It plays a vital role in industrial machinery, where precise power transmission and load control are essential. They find application in equipment such as generators, pumps, compressors, and industrial mixers. These clutches ensure smooth engagement under varying load conditions, protecting the machinery from excessive strain and preventing sudden jolts. By disengaging during overloads or stalling situations, they act as safety mechanisms, safeguarding both the equipment and operators.
- Lawn and Garden Equipment:
Centrifugal clutches are widely utilized in lawn and garden equipment, including lawnmowers, chainsaws, and brush cutters. These clutches enable efficient power transfer from the engine to the cutting blades or chains, ensuring optimal performance and reducing operator fatigue. By automatically engaging and disengaging based on engine speed, they enhance user control and safety while protecting the equipment from damage caused by excessive loads or sudden stops.
- Construction Machinery:
In the construction industry, centrifugal clutches are employed in various machinery such as concrete mixers, compactors, and concrete saws. These clutches enable smooth power transmission to the working components, ensuring efficient operation and productivity on construction sites. They offer the advantage of controlled engagement, allowing operators to start and stop the equipment easily, even under heavy load conditions. This enhances overall safety and operational efficiency.
- Recreational Vehicles:
Centrifugal clutches are integral to recreational vehicles such as ATVs (All-Terrain Vehicles) and snowmobiles. These vehicles often require quick acceleration and responsive power transfer to navigate challenging terrains. Centrifugal clutches provide the necessary torque and control, enabling smooth and precise operation. By engaging at the optimum engine speed range, they enhance performance, traction, and maneuverability.
- Agricultural Machinery:
Centrifugal clutches find applications in agricultural machinery, including tillers, tractors, and irrigation systems. These clutches facilitate power transmission to the various implements used in farming operations. By automatically engaging and disengaging based on engine speed, they optimize efficiency and protect the machinery from potential damage due to overloading. This ensures reliable and productive performance in agricultural settings.
- Industrial Power Transmission:
Centrifugal clutches also play a crucial role in industrial power transmission systems. They are employed in applications such as conveyor systems, industrial fans, and power take-off units. These clutches facilitate efficient power transfer from the prime mover to the driven equipment. By engaging and disengaging at the appropriate speed, they maintain optimal operational conditions, reducing wear and tear and improving overall system reliability.
In conclusion, centrifugal clutches have diverse applications in numerous industries. From automotive to industrial machinery, lawn and garden equipment to construction machinery, and recreational vehicles to agricultural machinery, these clutches provide efficient power transmission, controlled engagement, and protection against overloads. Their versatility and reliability make them indispensable components in systems that require optimal performance and user control.
Reference: Wikipedia