What is a Plant Layout ?
A plant layout is the arrangement of the physical elements of facilities ( or machines / equipment ) which make the product or service. This facilities layout is the overall arrangement of machines, men, materials handling, service facilities, and passengers required to facilitate efficient operation of production system.
Objectives of Plant Layout
The primary goal of plant layout is to maximize profits by the arrangement of all plant facilities to the best advantage of the total “manufacturing equation” – men, materials, machines, and money in fulfilling this goal.
Objectives of plant layout are :
- Minimize materials handling.
- Reduce the manufacturing cost.
- Afford economically output quantity and quality.
- Maintain flexibility of arrangement and of cooperation to meet changing needs.
- Maintain high turnover of work-in-process.
- Reduced investment in equipment.
- Make effective and economical use of floor space.
- Utilize equipment and facilities in the best possible way.
- Reduce work delays and stoppages.
- Promote effective utilisation of manpower.
- Avoid back-tracking.
Types of Layout
The pattern by which departments and facilities within departments are arranged may be viewed either in terms of work flow or the function of the productive system. According to work flow pattern, four basic types of layout are used in manufacturing operations.
Types of layout are following :-
- Fixed position layout
- Pricess or functional layout
- Product or line layout
- Group layout
Group layout is based on group technology philosophy is accepted as the fourth type of layout. In this type of layout an existing functional layout is converted to group layout to derive all benefits of product layout.
1. Fixed Position Layout
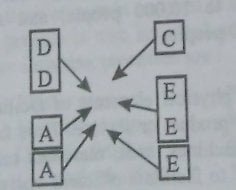
In fixed position plant layout, the product by virtue of its bulk or weight remains at one location. The equipment, personnel required for the product manufacture are removed to the product, rather vice versa. This layout is observed to be used under following conditions :
- When material forming or treating operation requires only tools or simple machines.
- When only one or a few pieces of an item are to be manufactured.
- When the cost of moving the major piece of material is high.
- When the skill of workmanship lies in the abilities of workers or when it is designed to fix the responsibility of product quality on one workman or group of workers.
Examples of this type of layout are : sound stages on a movie lot, aircraft, locomotive, ship assembly shops, shipyards, etc.
Advantages of fixed position layout are :-
- Handling of major assembly is a reduced.
- Highly skilled operators are allowed to complete their work at one point and responsibility for quality is fixed on one person or assembly crew.
- Frequent changes in product design and in sequence of operations are possible.
- The arrangement is adopted to variety of products and intermittent demand.
- It is more flexible almost in all respects.
2. Product Layout
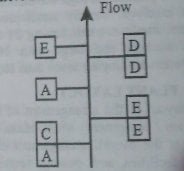
In product layout, the equipment or assembly work stations are arranged according to the progressive steps of sequence or operations by which the product is made. Product plant layout is used advantageously in the continuous-production system where :
- The number of end products is small.
- The parts are highly standardized and interchangeable.
- The volume of production for any item is high or large.
- The demand of the product is fairly steady.
- The continuity of material flow can be maintained.
This type of layout is exemplified in automobile assembly, food processing, and furniture manufacture.
Advantages of product layout
1. Reduced handling of material by transfer machines or conveyors.
2. Reduced amount of material in process, allowing reduced production time, and lower investment in materials.
3. More effective use of labour through :
(i) Greater job specialization.
(ii) Ease of training.
(iii) Wider labour supply.
4. Easier control.
5. Less inspection, less work-in-process, less floor area, and smaller aisles.
Disadvantages of product Layout are :-
- igher initial equipment investment.
- Greater vulnerability to work stoppage.
- Greater inflexibility due to changes in design, making it more costly.
- Greater boredom due to highly repetitive nature of work.
3. Process Layout

In process layout, all operations of the same type are grouped according to the general function they perform, without regard to any particular product. Conceptually, same type of operations are performed in the same area. For example, all drilling machines may be grouped together in one area, all milling equipment will be in another work center, and work involving spot welding is still another, etc. Refer Fig. 1.2.
The process plant layout is used advantageously where :
- Volume is low.
- Variety of products is many.
- The demand for the product is small or intermittent.
- General-purpose, low-cost machines are desirable.
- Machines or processing producing unwanted noise, vibration fumes, or heat can be located in isolated areas.
This type of layout is exemplified in custom jobshop, department stores, hospitals, etc.
Advantages of Process Layout are :
1. Better machine utilisation allows lower machine investment.
2. Adaptable to a variety of products and to frequent changes in sequence of operations.
3. Readily adaptable to intermittent demands.
4. Makes easier the continuity of product in the event of :
(i) Machine break-down.
(ii) Storage of materials.
(iii) Absent of workers.
5. Permits a maintenance.
6. Allows incentives pay system to individual workers to raise the level of their performance.
Disadvantages of Process Layout
- Operations cost per unit may be higher-often much higher because of the slow operation of the general purpose machines used.
- Work routing, scheduling and cost of accounting are costly due to separate costing of every new order.
- Materials handling and transportation costs are high since products follow different routes every time and use of conveyors becomes uneconomical.
- Inventories of materials in process are high and large storage space is required because of slow movement of materials.
- Difficult to keep a good balance between labour and equipment needs.
4. Group Layout
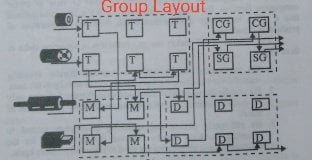
In group plant layout, the existing job shop/batch manufacturing shop is partitioned in a few groups of machines where each group produces its associated families of components. Group technology (GT) philosophy uses similarity of components from the processing point of view to create component families. By using the philosophy, a job shop is transformed into a group technology environment which facilitates optimization of product scheduling.
The essence of GT makes use on similarities in recurring tasks in three ways.
- By performing similar activities together thereby avoiding wasteful time in changing from one unrelated activity to the next.
- By standarizing closely related activities thereby focusing only on distinct differences and avoiding unnecessary duplication of effort.
- By efficiently storing and retrieving information related to recurring problems thereby reducing the search time for the information and eliminating the need to solve the problem again.
Fig shows how a job shop can be partitioned to GT shops. It can be noted that the four components are the representative components of the component families.
Advantages of Group Layout are following :
- Reduction in machine set-up time and cost.
- Reduction in material handling cost.
- Elimination of excess work-in-process inventory which subsequently allows the reduction in lot size.
- Reduction in through-put time.
- Simplification of production planning functions, etc.
Disadvantages of Group Layout are :
- Change of the existing plant Layout to GT layout is time consuming and costly.
- Inclusion of new components in the existing component families requires thorough analysis.
- Change of input component-mix may likely to change cell structure.
- Change in batch-sizes may change number of machines for any machine type.
- Existence of a large number of exceptional components leads to complexity in machine loading. Exceptional components are those which are processed by more than one machine groups.
Check Out Other Important Topics