Piston rings are small, metal rings that fit into grooves on the piston of an internal combustion engine. They play a vital role in the engine’s operation, sealing the combustion chamber, controlling oil consumption, and transferring heat from the piston to the cylinder wall.
In this article, we will take a closer look at piston rings, their design, and their function. We will also discuss the importance of piston rings and the signs that they may need to be replaced.
What are Piston Rings ?
A piston ring is a split ring in a reciprocating engine, such as an internal combustion engine or steam engine, that fits into a groove on the exterior diameter of a piston.
It is an expandable split ring used in Internal Combustion Engines to provide a seal between the piston and the wall of the cylinder liner.
Where are piston rings located on a piston?
Piston rings are located in grooves on the outer diameter of the piston. The number and type of piston rings vary depending on the engine design, but they are typically located in the following order:
- Top compression ring
- Second compression ring
- Oil control ring
The top compression ring is located closest to the piston crown and is responsible for sealing the combustion chamber. The second compression ring helps to support the top compression ring and provides additional sealing. The oil control ring scrapes excess oil from the cylinder wall and returns it to the crankcase.
Functions of Piston Rings
The main function of Piston ring is to seal the gases generated in the combustion inside the combustion chamber. It helps to transfer heat to the wall of the cylinder, and then to lubricate and scrape the oil out of it. Getting the right quantity of oil is vital for engine’s performance.
Too much oil will cause the engine to burn off during combustion, potentially causing your engine to produce blue smoke, and too little will ultimately cause the engine to seize. Lets discuss in detail about why piston rings are required.
Piston rings have three main functions:
1. To seal the combustion chamber
Piston rings create a tight seal between the piston and the cylinder wall, preventing combustion gases from leaking into the crankcase. This is essential for maintaining compression and preventing oil blow-by.
The top compression ring is responsible for sealing the combustion chamber. It is the first ring to encounter the combustion gases as the piston moves up the cylinder during the compression stroke. The top compression ring is typically made of a high-strength material, such as cast iron or steel, and it has a sharp edge that scrapes against the cylinder wall to maintain a tight seal.

2. To control oil consumption
Piston rings also help to control oil consumption by scraping excess oil from the cylinder wall and returning it to the crankcase. This helps to prevent oil from burning in the combustion chamber and forming harmful deposits.

The oil control ring is responsible for scraping excess oil from the cylinder wall and returning it to the crankcase. It is typically located below the top compression ring and has a series of slots or holes that allow the oil to drain back into the crankcase. The oil control ring is also made of a high-strength material, and it has a sharp edge that scrapes against the cylinder wall to remove excess oil.
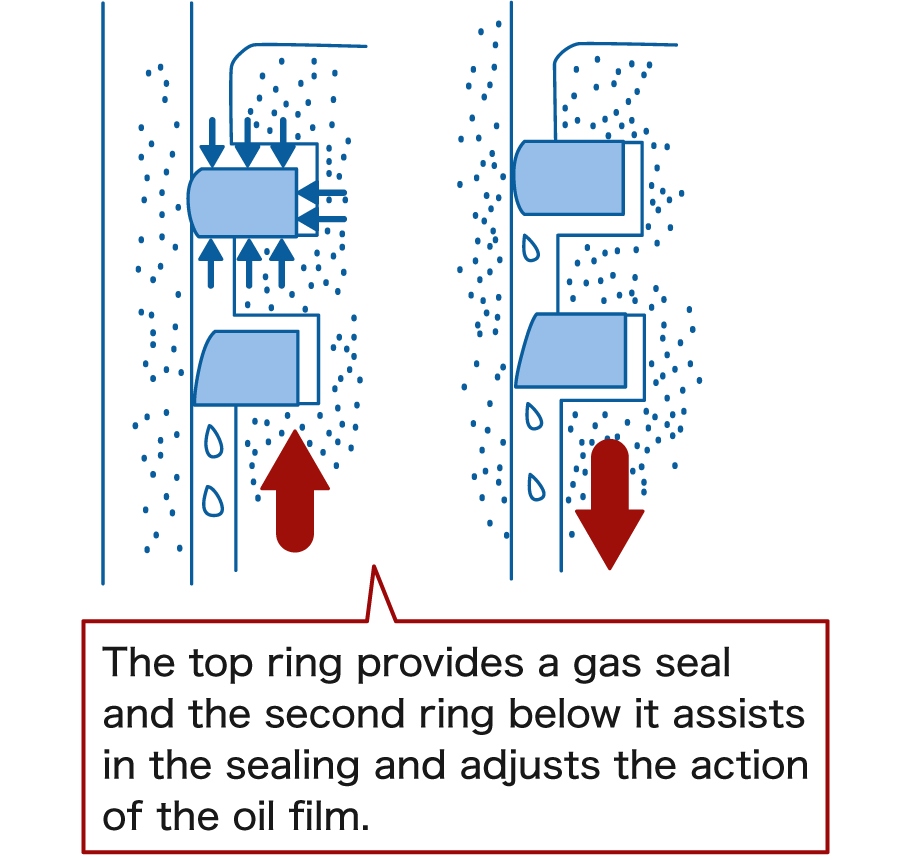
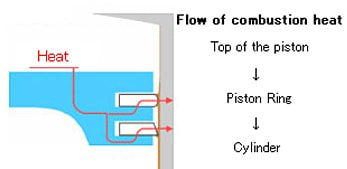
3. To transfer heat from the piston to the cylinder wall
Piston rings also help to transfer heat from the piston to the cylinder wall. This heat is then dissipated into the engine coolant, which prevents the piston from overheating. Without the piston rings, the piston would overheat, leading to engine failure.
When combustion of gas takes place inside the combustion chamber, temperature inside chamber near piston crown is approximately 300℃.The engine can be damaged if heat accumulated and that’s why heat needed to release and done by rings.
Piston rings also help to transfer heat from the piston to the cylinder wall. This is because piston rings have good thermal conductivity. As the piston moves up and down the cylinder, it transfers heat to the piston rings, which then transfer the heat to the cylinder wall. The cylinder wall has a large surface area, which allows the heat to be dissipated into the engine coolant.
4. Maintaining adequate oil quantities between the piston and the cylinder wall
A small amount of oil is poured over the pistons so that they travel smoothly, with little metal-to – metal friction. rings adjust the oil quantity/amount.
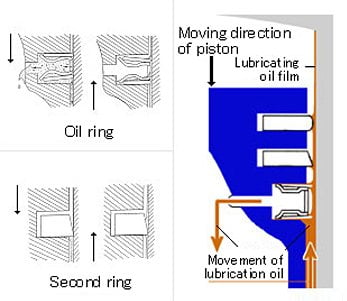
Rings need some lubricating oil for lubrication of cylinder wall, but it is desirable to keep this quantity to a minimum. The rings work in a scraping manner, keeping the excess oil out of combustion chamber s. In this way, oil use is kept at an appropriate amount and also reduce the amount of harmful emissions.
5. Provide Support piston in the liner
Piston rings support the piston in the liner by preventing it from wobbling. This is important because it helps to reduce friction and wear on the piston and cylinder wall.
Piston rings are designed to exert a slight outward pressure on the cylinder wall. This pressure helps to keep the piston centered in the cylinder and prevents it from wobbling.
In addition, piston rings help to support the piston by filling the gap between the piston and cylinder wall. This gap is necessary to allow for thermal expansion of the piston, but it can also create a point of weakness where the piston can wobble. By filling this gap, piston rings help to provide support for the piston and prevent it from wobbling.
The support provided by piston rings is especially important at high engine speeds. At high speeds, the piston is subjected to a lot of centrifugal force. This force can cause the piston to wobble if it is not properly supported. Piston rings help to prevent this wobbling and keep the piston centered in the cylinder.
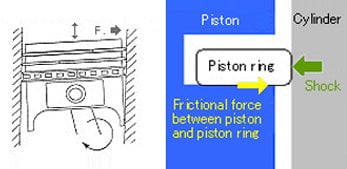
If the piston rings are worn or damaged, they will not be able to provide adequate support for the piston. This can lead to a number of problems, including increased friction and wear, reduced engine power and efficiency, and even engine failure.
6. Minimising the wear and tear of the wall of cylinder liner
Piston rings minimize wear and tear of the cylinder liner by reducing friction, scraping off excess oil, transferring heat, and supporting the piston. These functions help to keep the cylinder liner clean, cool, and free of deposits, which all contribute to extending the life of the engine.

Rings need some lubricating oil for lubrication of cylinder wall, but it is desirable to keep this quantity to a minimum. The rings work in a scraping manner, keeping the excess oil out of combustion chamber s. In this way, oil use is kept at an appropriate amount and also reduce the amount of harmful emissions.5. Maintaining adequate oil quantities between the piston and the cylinder wall.( Maintaining the proper amount of oil between the piston and the wall of the cylinder. )
A small amount of oil is poured over the pistons so that they travel smoothly, with little metal-to – metal friction. rings adjust the oil quantity/amount.
Material for piston rings :-
Piston rings are typically made from materials that can withstand high temperatures, resist wear, and provide an effective seal between the cylinder and piston. Common materials for piston rings include:
- Cast Iron: Traditional cast iron piston rings are widely used in marine diesel engines due to their good wear resistance and durability. Gray iron and ductile iron are common variants.
- Alloyed Cast Iron: Some applications may call for cast iron with alloying elements like chromium, molybdenum, or nickel to enhance specific properties such as hardness and heat resistance.
- Nitrided Steel: Steel piston rings that undergo nitriding, a surface-hardening process, are chosen for their increased hardness, wear resistance, and improved performance under high temperatures.
- Stainless Steel: Stainless steel rings offer corrosion resistance and durability. They are suitable for marine environments where exposure to seawater is a consideration.
- Chrome-Plated Rings: Chrome-plated piston rings provide enhanced wear resistance and reduced friction. The chrome coating helps protect against corrosion and wear.
- Ceramic-Coated Rings: Ceramic coatings, such as those containing materials like silicon nitride or chromium oxide, provide exceptional hardness and resistance to wear. These coatings are often used in high-performance marine diesel engines.
- Molybdenum (Moly) Coated: Molybdenum coatings on piston rings improve lubrication, reduce friction, and enhance wear resistance. This can be beneficial in marine diesel engines operating under varying loads and conditions.
- Phosphated Rings: Phosphate coatings on piston rings help improve initial wear characteristics and provide better oil retention.
- Nimonic Alloy: In some specialized marine diesel engines, piston rings may be made from high-temperature alloys like Nimonic for superior heat resistance and mechanical properties.
The choice of material depends on the specific requirements of the engine, including operating conditions, performance expectations, and the type of fuel used. Engine manufacturers carefully select piston ring materials to ensure optimal performance and longevity under various conditions.

Why piston rings clearance are necessary ?
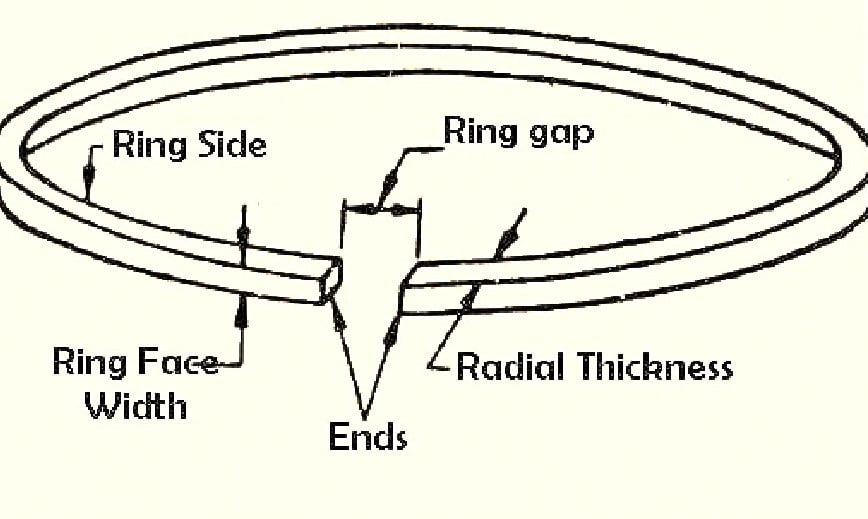
Piston ring clearance is essential in internal combustion engines to account for various factors, and it is commonly categorized into axial (vertical) and circumferential (horizontal) clearances.
Axial Clearance:
Axial clearance refers to the space between the top and bottom edges of the piston ring and the corresponding surfaces on the piston. This clearance is critical for accommodating thermal expansion, manufacturing tolerances, and dynamic movements during engine operation. As the engine heats up during combustion, both the piston ring and the cylinder block undergo thermal expansion.
Without sufficient axial clearance, the expanding materials may bind or stick, potentially leading to increased friction, wear, and loss of engine efficiency. Additionally, manufacturing processes can introduce small variations in the dimensions of the piston rings and cylinder bore. Adequate axial clearance ensures that these variations do not result in interference, maintaining a proper seal for combustion gases and preventing issues such as scuffing.
Axial clearance for large engine : 0.4 mm for top rings & 0.2 mm for lower rings.
Circumferential Clearance:
Circumferential clearance, also known as end gap, refers to the space between the ends of a piston ring when it is installed in the piston groove. This type of clearance is crucial for accommodating the dynamic movement of the ring during engine operation. Piston rings experience reciprocating and rotating motions as the piston moves up and down within the cylinder. Circumferential clearance allows the ring to expand or contract slightly as it moves, preventing binding and reducing the risk of wear. In situations where there is insufficient circumferential clearance, the ring may encounter increased friction against the cylinder walls, leading to potential damage and reduced engine efficiency. On the other hand, excessive circumferential clearance can result in inadequate sealing, allowing excessive oil consumption and reducing compression.
Circumferential clearance for a large engine : 0.5 % of cylinder diameter (moderate ratings ) & 1.0 % of cylinder diameter (higher ratings )
Both axial and circumferential clearances play integral roles in maintaining the proper functioning of piston rings within an engine. They collectively contribute to effective sealing, accommodating thermal expansion, facilitating dynamic movements, and ensuring longevity and reliability.
What will happen if excessive wear of rings
Excessive wear will reduce engine efficiency and may cause
- Hot gas to blow past the rings.
- Removing lubricating
- Causing ring distortion and breakage.
Types of piston rings
There are mainly two types of piston rings.
- Compression rings
- Oil Control rings
Generally, there is confusion among people regarding the number and types of rings. Let’s get first clear about the number of rings.
The Number of piston rings
Depending upon the requirements, the number of rings used on a piston varies. Earlier engines used two or four compression rings and one or two oil control rings. Nowadays, for modern IC Engines having lower height , manufacturers limit the number of rings to three. Out of these Two – Compression rings. One – Oil Control rings. One in the top groove, the other in the second groove and an oil ring in the third groove. Often a scraper ring is installed as the second ring or lower compression ring.
Why we use Two or more Compression rings.
Due to the high-pressure difference between the combustion chamber and the crankcase, a minimum of two compression rings is necessary. This difference in pressure could be as high as 70 bar. If we use one ring ,then it cannot withstand such high pressure that’s why manufacturer uses two or more compression rings instead of one. The Increase in the number of rings also decrease the pressure b/w the rings and walls of the cylinder liner. It reduces wear and increase the life of the engine.
Types of Piston Rings
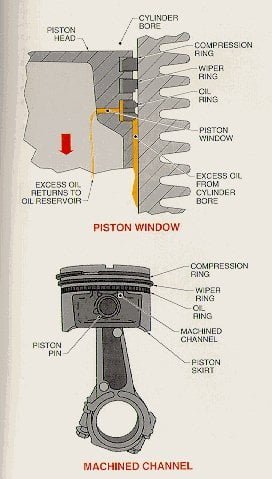
1. compression ring :-
Locations :- It is generally placed at the top of the head of piston and side of the piston.Or,They are places immediately after below the head of the piston.Functions :-rings for sealing the gases above the piston and preventing gas leakage.It is called compression rings or pressure rings or sealing rings.Those most commonly used being of the rams bottom type.Materials :- This is ring made of cast – iron with a uniform section either square or rectangular inside of the pistol being hammered.Number of compression rings :-The number of compression rings depend on type of engines and it’s design but nowadays mostly two compression rings used.Cross-section :- The cross-section of compression rings is eitherA) Rectangular or,B) wedged shapeWith a tapered face.A thin bearing edge presents on tapered face which helps in reduce fiction and wearing and provide provide proper sealing.
Wiper rings :-
It is also known as Napier ring ,Scrapper ring or Back up compression rings.It is type of compression rings fitted just below the top compression rings.
Locations :-
It is fitted Next to Compression rings.Or we can say thatThis rings have a tapered face located in the ring groove between the compression ring and the oil control ring.
Functions :-
The wiper ring is used to 1.further seal the combustion chamber.It act as a support back up ring because Combustion gases that pass by the compression ring are stopped by the wiper ring. and2. to wipe the cylinder wall clean of excess oil and also did the work of smearing the oil on the wall of cylinder ensuring that compression rings are properly lubricated.Construction :-Most of the wiper rings have a taper angle face that is positioned towards the bottom to provide a wiping action as the piston moves towards the crankshaft.What will happen if wiper ring installed incorrectly ?If the wiper ring is improperly placed with a tapered angle nearest to the compression ring, this causes in excessive oil consumption. This is caused by wiper ring because it wiping the excess oil towards the combustion chamber.
2.Oil control rings :-
As the name suggests,It is used regulate the amount of oil on the wall of cylinder liner when piston goes up and down.
Locations :-
It may be fitted below the compression rings on the Piston, or alternatively to the skirt.Or, we can say that this is placed at the bottom of piston, from the crankcase side.Or ,in some engines it is installed immediately after the compression rings and above the piston bores.For larger engines ,one more control rings fitted on part of skirts.
Functions :-
The main functions of oil control rings is used to control the amount of lubricating oil used in IC engines.It also did the work of ensuring oil spreading evenly on the wall of the cylinder & scrap excess amount of oil off the wall and return it to crankcase.This ring do not allow lubricating oil to get past b/w the cylinder wall and piston.
Cross-section :-
Their cross-section is shaped with a downwards wedge or lip which spreads the oil on the upstroke of the Piston but scrapes off excess oil on the downstroke.There is holes or slot found in the radial centre of oil control rings.Rings, called drain holes which allow rapid removal of oil to the back the ring groove from where it can pass through the holes to the inside of the skirt and finally to the crankcase.
Materials :-
For improved life the scrapping edge may be chromium plated.
Piston Rings Installation
Before installing rings first checks new ring or spare rings.The marking of new rings checked and compare it with old one for the same grade or position.If the old marking of the piston ring is wiped out, check the piston ring manual for exact size of rings so that it can be put in its proper groove.Clean the piston :-Thoroughly clean the pistons and extract any traces of carbon oil from the ring grooves. Remove the carbon using a twist drill and tap wrench from the oil return bores; clean the grooves without damaging the sides of the groove. Replace cracked pistons, collapsed and wornCylinder cleaning :- Remove all carbon residue from the top surface of the cylinder bore that shows no wear.rings inspection :-The groove must be cleaned properly to ensure that there is no carbon and sludge deposit in the groove. While cleaning, it should be kept in mind that some of the piston grooves are coated with a special protective film. They should not be damaged by the use of chipping or grinding tools.If a distance of 0.12 mm or more is measured between the new parallel-sided compression ring and the corresponding groove side, the piston shall be excessively worn and replaced.Groove gap. piston usabilityCylinder inspection :-The cylinder (top ring reversal bore wear) must be replaced if the cylinder wear is greater than 0.1 mm in petrol engines and 0.15 mm in diesel engines.

After cleaning the groove s properly,the rings is inserted in the respective grooves by using piston rings tools or itting tools.This tool use for expanding rings and it is fitted in the grooves by sliding it from the top of the piston head.Ensure that the ring is inserted, keeping the top marking on the upper side. Most piston rings are marked “TOP” or the surface stamped identification number is considered to be the top face if there is no specific marking.
- Apply plenty of oil to the sleeve, piston, piston rings, and connecting rod bearings.
- Then place the sleeve over the piston with extreme care to pretension the rings.
- Once the cylinder is oiled, you can then insert the pistons in the proper direction of installation. Check once again if everything is correctly aligned. The sleeve must lie on the block. Finally, carefully push the piston into the cylinder.
Once the piston rings have been installed, it must be ensured that they can move freely. Rotate the joint ends of the piston rings by 120 °.
Piston rings expander
It is a special types of tool used to remove and install rings with minimum ring distortion.
The use of the ring expander will significantly reduce the missalignment of the ring point, which may be detrimental to good ring sealing and engine performance.
It is extremely important to use the ring expander tool appropriately as wrong use may damage the ring or it may hurt the operator as the ring is under constant tension.
In small 4 stroke engines, in case the tool is not available, the ring can be expanded by use of clothes or rags available in the engine room. Two rags are placed on each side of the ring ends and they are pulled so that rings can be expanded and inserted from the top of the piston.
Piston rings compressor tool
The piston ring compressor is a special tool that is specifically designed for compressing the piston rings when a piston is re-installed. This is done by opening the piston ring compressor enough so that the piston can slip into the opening.Then the rings compress by tightening the tool to make it snug around the piston. The piston ring compressor can be tightened by turning the adjusting arm clockwise and loosened by turning the adjusting arm clockwise while holding the release spring down as shown below.It is important to lubricate both the piston ring compressor and the oil bore of the cylinder before trying to push the piston down into the cylinder.
How do piston rings work
Earlier ,I have explained different types of rings and their uses.Working of rings means ,how these rings work their functions during process of combustion.The topmost groove of the piston consists of a compression ring, the main purpose of which is to seal any kind of leakage within the combustion chamber during the combustion process. As the air-fuel mixture is ignited, the combustion gas pressure is applied to the piston head, pushing the piston to the crankshaft.Pressurized gases pass through the gap between the wall of the cylinder and the piston and through the ring groove of the piston. During the combustion process, the force of high-pressure gases forces the piston ring against the cylinder liner rim, which helps to form an effective seal. This pressure on the piston ring is proportional to the combustion gas pressure.The next set of rings in the piston that are located below the compression ring and above the oil rings are called wiper rings.
They have a tapered face construction and are used to further seal the combustion chamber. As the name suggests, they help extract any residual oil and impurities from the liner wall. If some of the combustion gases could pass through the compression ring, these gases would be blocked by the wiper ring in good condition.The last set of rings are the oil rings that are found in the bottom grooves of the piston nearest to the crankcase. The main purpose of the oil ring is to scrape any excess oil out of the walls of the cylinder liner while the piston is in motion. Most of the oil that has been cleaned is directed back into the crankcase to the oil sump. These oil rings come with a spring mounted on the back of the 4-stroke engine to provide an additional push for cleaning the liner.
Marine Diesel Engine Piston Rings
4 – stroke Trunk type engines
The requirements of piston rings in 4-stroke type engines is different because the assembly of piston liner is directly open to the sump.
Thus,oil-scraper rings additionally needed in the piston ring – pack.Typically,the number of rings is 2-5 , depending upon the type and specifications of engine.Usually, 2-4 compression rings are equipped to seal the gases from the combustion chamber and 1-3 oil control rings are provided to prevent excess oil from entering the combustion chamber.For marine diesel engine
The number of compression rings :-4 to 5And oil control rings :- 1to 3One more oil control rings in the skirt below the gudgeon pin.But in automotive engine :-Compression rings :-2
Oil control rings :- 1
2stroke marine diesel engine piston Rings
Generally,The number of piston rings in 2 – stroke diesel engines is 5.
But , number also depends upon the size and types of engines.For e.g an RTflex 35 will have a very short skirt and is equipped with three piston rings, but an RTA engine may have 5 piston rings.The combustion chamber of a 2 stroke marine diesel engine is a large space generating a tremendous amount of heat and stresses. The upper rings of the piston are directly in contact with the combustion chamber, hence they need better protection and coating to tackle the thermal stress and provide proper sealing.
Piston Rings Coatings
Wear resistance coatingsPlasma Coating (using a plasma spraying method where a gas
mixture is directed through an electric arc generated between a tungsten electrode and a water cooled copper tube to create a plasma state” at 10,000 to 15,000 deg. C). This plasma state melts and fuses any metal, with gas molecules and atoms
disassociating.Chrome plating: It is a hard outer galvanic chrome layer. Double
chrome plating is done an bath sides of the ring. This increases the
wear and corrosion resistance.Tungsten carbide coating which gives a better wear resistance.Running-in Coatings
These are soft coatings such as copper, graphite or phosphate which
are meant to wear quickly and give the ring a similar profile as the liner.For large two stroke marine diesel engine , many new designed for piston rings were introduced.Some of important designed discussed below :-Main engine :-
CPR (controlled pressure relief ) Rings :-
The topmost rings is controlled pressure (cpr ) relief rings.
This rings have six controlled pressure relief grooves (oblique hallow grooves ) cut across the face.This ensures even pressure distribution and decrease of thermal load to the second ring as well as the liner.It has s type joints at the rings end or we can say that ring has one double lap s-seal.A new design has also recently been introduced, a modified version of the CPR rings known as CPR Port on Plane rings (CPR POP). In this types of rings, the only modification done is that they placed the position of grooves in the lower side of rings,as it was noted that the wear of the CPR ring grooves on the running side was faster than usual.
Second or Intermediate Rings:
The other rings have an oblique cut at the ends of rings. All the piston rings are aluminium-coated on the outer surface for helping in running-in.
Wartsila engine :-
In the Wartsila 2 stroke engine, the piston ring grooves on the surface of the piston are hardened for excellent wear resistance. The top piston ring (also known as the Gas Tight (GT) ring in Wartsila) has overlapping ends to avoid gas leakage with an asymmetrical barrel shape. They are chromium-ceramic (CC) coated with a running-in coating (RC).
Piston Cleaning Ring
It is the ring which is embedded in the top edge of the liner just below
the cylinder head level. Its purpose is to remove the excessive carboneous deposits at the top-land portion of the combustion chamber wall which would otherwise contaminate and affect lubrication.
Anti-Polishing Ring
It is the ring which reduces the polished effect of the liner wall, which is formed due to the hard deposits from combustion in contact with the liner.
Polishing is unwanted, since it does not allow oil film retention on the liner wall, and the oil passes over the ring pack portion to the combustion area
when it is burnt and wasted. Polishing depends on oil feed rate, excessive peak pressures, ting and liner materials, and an increase in combustion hard products at liner-ring interface.
Piston rings failure
Inside the combustion chamber,there is tremendous amount of temperature and pressure available during combustion.If there is unusual change in pressure and temperature inside combustion chamber, it causes problem in performance of rings I.e (efficiency of engine )The reason of unusual change in combustion chamber is1.detonation and pinging of the fuel from the leaky injector or when the fuel is mixed with dirty air.2.Contaminated fuel oil or incorrect grade of cylinder oil would also affect the performance of the ring. As the ring starts to wear down , their ability to seal combustion gases will become apparent.3.Bad fuel or cylinder oil quality, poor combustion process, incorrect fuel timing, worn liner etc. are the normal cause of piston rings worn out. The most common indication or sign of a worn ring is gas passing through the crankcase or under the piston region known as blowby.4.Sticky ring due to carbon or sludge deposit and breaking or crack on the ring can result due to wear down.
Life span of piston rings
All machines have a fixed periods for overhauling and replacement.So,rings have also fixed time.But The life of a rings entirely depends on the
1. ring type,
2. the size of the engine it is fitted on,
3. and the operational condition of the ring and the liner.For a large 2-stroke diesel engines having approximately Bore diameter 900 mm has life up to 24,000 hours.And small engines having bore diameter 500 mm has life up to 16,000 hours.The rings of Four stroke marine auxillary diesel engines having medium high speed have less life than 2 stroke engine.The avg. lifespan of a marine four stroke high-speed engine is approximately 8000 hours, post which renewal is required.



It’s nice that you talked about how piston rings could seal the gases generated in the combustion inside the combustion chamber. I was checking out my friend’s mechanical engineering schoolbook the other day and read some parts about piston rings. From what I gathered, it seems there are servo motor piston rings too.