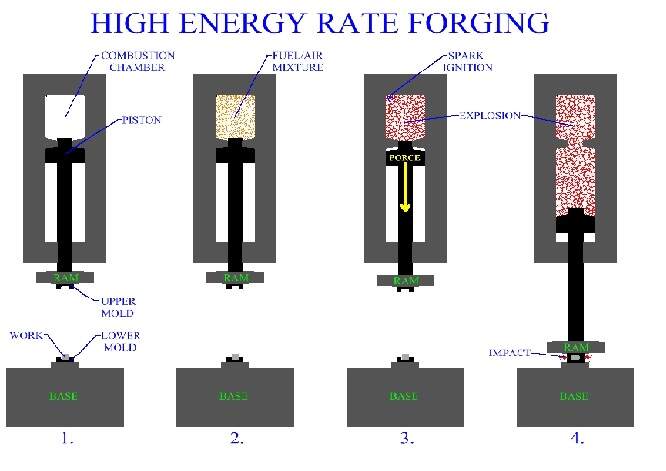
In this article we are going to discuss about various types of woodworking machines that forms and essential part in carpentry shop. Lets start with defining woodworking machines.
Modern carpentry shop, in addition to the hand tools described earlier, requires the use of some power-driven machines, particularly where largescale production is to be obtained. The size and capacity of the machines used depend on the size of the general run of the work to be done. Machines chosen for carpentry shop must be well built, and their accuracy should be dependable. They should be well guarded to protect the worker from the hazards of operation.
What are woodworking machines ?
The woodworking machines are the machine designed to work with wood. These machines, which are typically powered by electric motors, are widely used in woodworking. Grinding machines (used for grinding down to smaller pieces) are sometimes included in the definition of woodworking machinery.
The machines commonly used are briefly described below.
1. Woodworking Lathe
The woodworking lathe is one of the most important machines used in a carpentry shop. This is employed primarily for turning jobs in making cylindrical parts. However, by suitably manipulating the tools, tapers, radii, and other irregular shapes can also be easily turned.
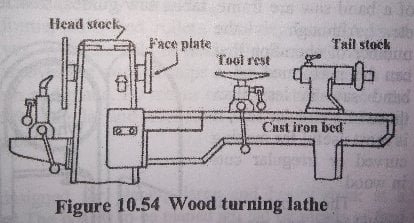
It resembles the engine lathe most frequently used in the machine shop, and consists of a cast iron bed, a head stock, tail stock, tool rest, live and dead centers, and a speed control device (Fig. 10.54). The drive, in modern lathes, is individual motor driven ; and a cone pully on the head stock spindle is connected by a belt to a cone pully on the motor shaft.
In practice, the workpiece is either clamped between two centers or on a face plate. Long jobs are held between the centers and turned with the help of gouge, skew chisel, parting tool, etc. Generally, the lathe is supplied together with a number of accessories for making it useful for a variety of jobs. The size of lathe woodworking machines, as in the engine lathe, is usually specified in terms of the so-called “swing” of the lathe and the maximum distance between centers.
2. Circular Saw
Probably the second most important of single woodworking machines in a carpentry shop is the circular saw. It can be used for ripping, cross cutting, mitering, beveling, rabbeting, and grooving. Although there are many types of circular saws such as universal saw, variety saw, bench saw, the basic working parts are common to all. Each has a flat surface or table upon which the work rests while being cut, a circular cutting blade, cut-off guide, and a ripping fence that acts as a guide while sawing along the grains of the wood.
The circular saw usually has provisions for tilting the table upto an angle of 45° to enable the machine to cut at different angles required during mitering, levelling, etc. The size of a circular saw is determined by the diameter of the saw blade.
3. Band Saw
The next woodworking machines are band saws. The band saw is designed to cut wood by means of an endless metal saw band that travels over the rims of two or more rotating wheels. Other parts of a band saw are frame, table, saw guides, saw tensioning arrangement, etc. Although the number of operation that can be performed on a band saw is less than those of a circular saw, it is most useful for making curved or irregular cuts in wood.

The band is available in two models, vertical and horizontal. In the former, two wheels are arranged side by side and the table is mounted underneath. In the latter model, Frame illustrated in Fig. 10.55, the wheels are arranged one above the other in a vertical plane below the table and the band passes through the table. As in the case of the circular table, angular cuts are obtained by tilting the saw table. The size of the band saw is specified as the distance from the saw band to the inner side of the frame. The distance is roughly equal to the diameter of the wheels.
4. Jig Saw or Scroll Saw
The jig saw, which is also known as a scroll saw, is used for making intricate and irregular cuts on small jobs. On thin wooden pieces, jig saw can cut in a curvilinear path. These woodworking machines are actually a type of band saw of much smaller size and specially adapted to irregular work.
It consists of a base, frame, table, upper and lower chucks, guide assembly, and blade. Chucks hold the blade with its teeth pointing downward. The blade resembles a hand hacksaw blade in regard to its shape. The blade reciprocates vertically up and down and shapes the wood. The table of the jig saw can be tilted for angular work. The special feature of the saw is that it can be used to cut inside curves. A jig saw is specified by its blade-to-arm distance.
4. Jointer
A jointer is used for planing straight edges and surfaces of boards. In practice, it performs the work of a hand planer and is capable of producing a true surface with sufficient accuracy and speed.
In consists of a frame, table, feed rollers, revolving head fitted with two or three cutter knives. With the help of feed rolls, the plank is fed to the cutter head which removes the wooden chips as the board advances and makes its surface smooth and plane. By means of an adjustable fence, the jointer can also be used for angular and level cuts. A jointer is specified by the length of the cutting blade.
5. Wood planer
The next woodworking machines is wood planer which is designed for planing large and heavy stock at a comparatively faster rate. The boards to be planed are fed by means of feed rolls along a table against a revolving cutter head. The cutter head is mounted on an overhead shaft which is adjustable for regulating the depth of cut . The table of the planer is much wider and longer than that of a jointer for accommodating large and heavy stock.
6. Mortiser
A mortise is a square slot cut in the direction of depth for the purpose of making a mortise and tenon joint in a wooden piece. The mortising woodworking machines are used for cutting mortise and tenon joints which are very laborious and time consuming operations. There are three types of mortisers, namely (1) hollow chisel mortiser (2) chain mortiser and (3) oscillating bit mortiser.
A. Hollow Chisel Mortiser
The hollow chisel mortiser, the most commonly used woodworking machines, consists of a revolving spindle carrying an auger bit at the bottom end. The auger bit rotates at a high speed inside a hollow chisel of square section. When the chisel is forced into the wood, the bit bores a square hole by the sharp end of the chisel, the auger bit and chisel thus work together and perform boring of a square hole. The depth of the mortise is regulated by means of an adjustable depth stop. The spindle is rotated by an electric motor, and tool-feed is obtained by pressing foot-lever.
B. Chain Mortiser
The chain mortiser is primarily used for making mortises in doors and windows. It carries an endless chain which has saw type teeth on its outer surface. The chain revolves around a guide bar and cuts the stock. The mortise of the desired length is produced with round bottom corresponding to the profile of the revolving chain.
C. Oscillating Bit Mortiser
The oscillating bit mortiser carries a oscillating router bit and produces comparatively small mortises suitable for small cabinet and chair work.
7. Sanding Machines

Sanding is the operation of finishing wooden items after they have been machined. Essentially, a sanding machine performs a sand papering job to produce a uniformly sanded surface. Three common types of sanding machines are :
- Belt sander
- Spindle sander
- Disc sander
Belt Sander
It has an endless cloth backed abrasive belt which runs over two drums and is used for sanding and shaping flat surfaces. One of the drums is rotated by an electric motor and serves as the driver, while the other supports the belt and keeps it in proper tension. For sanding work by the abrasive belt, the the workpiece is supported by an adjustable table that may be tilted to any desired angle.
Spindle and Disc Sanders
They are employed for curved surfaces and use abrasive disc and vertical abrasive spindle. During operation, the disc or the spindle as the case may be, rotates and performs the work.
8. Grinder
A small tool grinders are a must woodworking machines in shops for sharpening and shaping various tools used in the shop. The grinder has two grinding wheels fastened on to the two ends of a rotating spindle which is driven by a small electric motor. Generally, one of the wheels is used for coarse grinding while the other for fine grinding. Sometimes one of the wheels, particularly which is softer, is provided with a wet-grinding attachment.
These were the different types of woodworking machines that are described here. Hope you liked the article. Please give your feedback in the comment section below.
Check Out Other Important Topics
Foundry Tools And Equipment – List, Names & Images
Sand Testing Methods – Full Process
Types of Casting Defects – Complete Overview
Moulding Sand – Properties, Types, Process, MCQs
Plant Layout – Types, Objectives, Principles, Advantages
| IC Engine | Important PDFs | Boilers | Synergy Maritime Exam | Naval Arch | MEO Class 4 |
| Interview Questions | Difference Between | Types of Pumps | Auxiliary Machines | Types of Valves | Home |