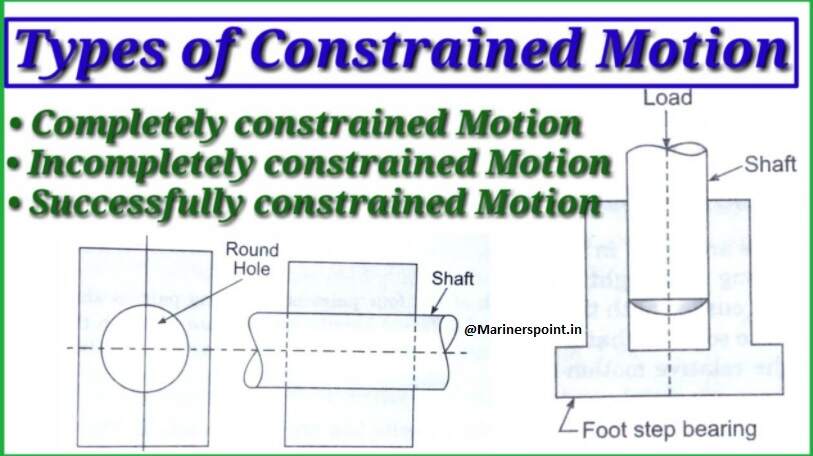
The jigs and fixtures are the economical means to produce repetitive type of work by incorporating special work holding and tool guiding devices.

Definitions of Jigs and Fixtures
Jigs and fixtures are devices that help in increasing the rate of identical parts while decreasing the amount of human effort required to produce these parts. It has already been stated that a center lathe is a suitable machine tool for producing individual parts of various shapes and sizes, but its use for producing similar articles in large quantities will be inefficient.
The definition of jigs and fixtures are given below :-
Jigs
Jig : A jig is a device that holds and locates a workpiece as well as guides and controls one or more cutting tools. The work is held and the tools are guided in such a way that they are in true positions relative to each other.
A jig is a plate, structure, or box made of metal or, in some cases, nonmetal that has provisions for holding the components in identical positions one after the other and then guiding the tool in the correct position on the work in accordance with the drawing, specification, or operation layout.
In other words, this is used for both holding the tools and guiding the cutting tools.
A jig’s main purpose is to provide repeatability, accuracy, and interchangeability in the manufacturing of products.
Some important things to remember about Jigs:
- It is used in unidimensional machining processes such as drilling, tapping, and reaming, among others.
- This system is light and has a complex shape.
- Gauge blocks are not required, and the cost of jigs is higher.
- Jigs are not fixed to the machine table until a large operation is required.
Fixtures
A fixture is a device that holds and locates a workpiece during an inspection or manufacturing process. The fixture does not act as a guide for the tool. Fixtures in construction are various standard or specially designed work holding devices that are clamped on the machine table to hold the work in position. The tools are adjusted manually or with gauges to the required position on the work.
In other words, fixtures are simply work holding devices that hold, support, and locate the workpiece in the desired position for any operation.
The primary function of fixtures is to hold and locate the workpiece during any machining operation, as well as to provide repeatability, accuracy, and interchangeability in product manufacturing.
Some key points about fixtures:
- Fixtures are used in multi-dimensional machining processes such as milling, grinding, and turning.
- This system was discovered to be heavy in weight and to have a simple design.
- Gauge blocks are provided for easy handling, and the price is reasonable.
- Fixtures have specific tools that are used in milling machines, shapers, and slotting machines.
- The fixtures are attached to the machine table.
Difference Between Jigs and Fixtures
The following are the fundamental differences between jigs and fixtures.
1. A fixture holds and position the work but does not guide the tool, whereas a jig holds, locates and as well as guides the tool.
2. The fixtures are generally heavier in construction and are bolted rigidly on the machine table, whereas the jigs are made lighter for quicker handling, and clamping with the table is often unnecessary.
3. The fixtures are employed for holding work in milling, grinding, planing, or turning operations, whereas the jigs are used for holding the work and guiding the tool particularly in drilling, reaming or taping operations.
Difference Between Jigs and Fixtures in Tabular Form
| Jig | Fixture |
| It guides the cutting tool. | It does not guide the cutting tool. |
| It is mostly attached to the machine table. | It is always attached to the machine table. |
| Jig is generally lighter than the fixture. | Fixture is generally heavier than the Jig. |
| Jig feet is used in its construction. | No such feet is used in its construction. |
| Bushes are used in a jig for guiding the cutting tool. | Bushes are not used in fixtures. |
| It is specially used for drilling, reaming & boring operations. | It is specially used for milling, turning, grinding operations. |
| Jig is widely used on drilling machine. | Fixture is widely used in milling, grinding machines. |
| Jig is costlier. | Fixture costs less as compared to the jig. |
| Complex designing. | Less complex designing. |
Elements of Jigs and Fixtures
The main elements of jigs and fixtures are following :-
1. Body :- It is a plate, box, or frame structure in which the machined components are located. It should be very strong and rigid.
2. Locating elements :- These elements did the work of locating the workpiece in the proper position in relation to cutting tool.
3. Clamping elements :- These components firmly secure the workpiece in the desired position.
4. Grinding and setting elements :- These elements of jigs and fixtures guide the cutting tool in the case of a jig and aid in proper tool acting in the case of a fixture.
5. Positioning elements :- These elements include various fastening devices used to secure the jig or fixture to the machine in the proper position.
6. Indexing elements :- They aren’t always provided. However, many workpieces may need to be indexed to different positions in order to perform machining operations on different surfaces or in different locations. In such cases, these elements must be incorporated into the jig or fixture.
Components
The actual component or the workpiece should be procured and studied for deciding the sequence of operations to be performed and evaluating the other designing details of the jigs and fixtures. One of the work surface is machined to act as the datum surface from which all other measurements are taken.
Types of Jigs and Fixtures
The quality, type and complexity of jigs and fixtures used depends on the type of work to be machined and the scale of production required to simple dive drinks are described below.
Types of Jigs
- Template jig
- Plate jig
- Channel jig
- Diameter jig
- Leaf jig
- Rung jig
- Box jig
1. Template Jigs
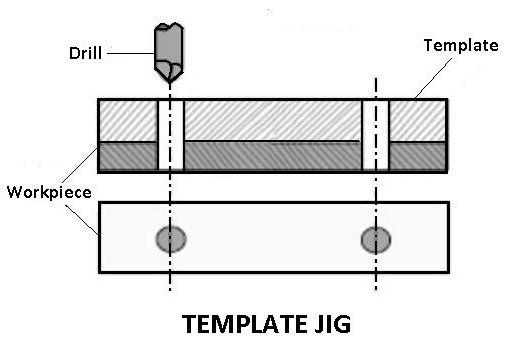
The template jig is the simplest of all the types of jigs. The plate, which has two holes, acts as a template that is fixed to the component to be machined. The drill is guided through the template’s holes, and the required holes are drilled on the work-piece at the same relative positions as on the template.
2. Plate Jigs

A plate jig is an improved template jig that incorporates drill bushes on the template. The plate jig is used to drill holes in large parts while keeping them accurate in spacing.
3. Channel jig

A channel jig is a simple jig with a channel-like cross section. The component is inserted into the channel and clamped by rotating the knurled knob. The drill bush is guided by the tool.
4. Diameter Jigs

A diameter jig is a tool for drilling radial holes in a cylindrical or spherical workpiece.
Figure 1 shows the diameter jig. The work 1 is placed on the fixed V-block 6 and clamped by the clamping plate 7, which also serves as a work locator. The tool is guided through the drill bush 8, which is positioned radially with respect to the work.
5. Leaf Jig
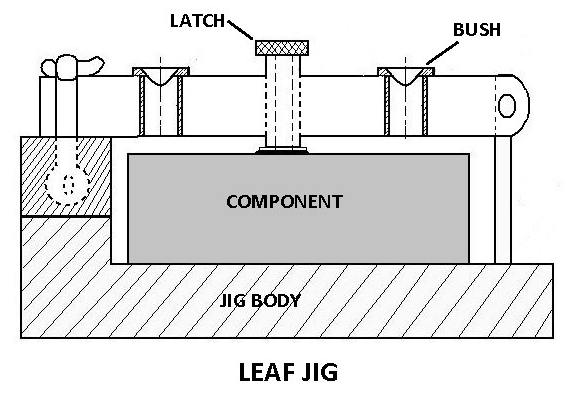
The leaf jig has a leaf that can be swung open or closed on the work for loading or unloading.
The leaf jig is shown in the figure above. It has a leaf or plate 13 hinged on the body at 11, and the leaf can be swung open or closed on the work for loading or loading purposes. The work 1 is located by the buttons 10 and is held in place by set screws 12. The drill bush 3 directs the tool.
6. Ring Jig

A ring jig is used for drilling holes in the circular flanged parts. The work is securely clamped to the drill body, and the holes are drilled by guiding tool through bushes of drill.
7. Box Jig

A box jig is a box-like structure that rigidly holds the work so that it can be drilled or machined from different angles at a single setting depending on which face of the jig is turned toward the tool.
Types of Fixtures
Following are the types of fixtures :-
1. Turning Fixtures
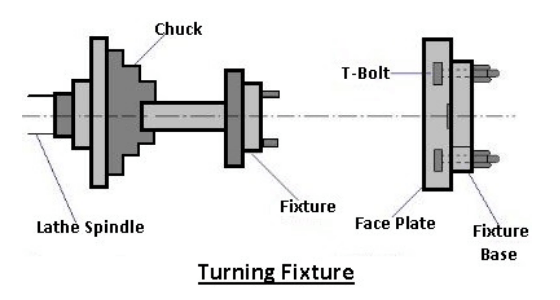
These fixtures are typically mounted on the machine spindle’s nose or a faceplate, and the workpieces are held in place by them. When necessary, the fixture may require a counterweight to balance the unbalanced fixture.
2. Milling Fixtures

Milling fixtures are typically mounted on the machine spindle’s nose or a faceplate, and workpieces are held in place by them. The table has been shifted and positioned correctly in relation to the cutter. Before beginning the operation, the workpieces are placed in the fixture’s base and clamped.
3. Broaching Fixtures

Broaching fixtures are used on various types of broaching machines to locating, holding, and supporting the workpieces during operations such as keyway broaching, hole broaching, etc.
4. Boring Fixtures

This fixture incorporates almost all of the prevalent principles of jig and fixture design; their construction does not need to be as sturdy as that of milling fixtures, because they do not have to bear as heavy cutting loads as milling fixtures, because they do not have to endure as heavy cutting loads as milling operations.
5. Grinding Fixtures
Fixtures of various types are used in grinding machines to locate, hold, and support workpieces during operations. These fixtures could be standard work-holding devices like chucks, mandrels, shaped jaw chucks, magnetic chucks, and so on.
A vertical surface grinder with a rotary table, for example, will typically have a rotary fixture secured to its table. Similarly, on a surface grinder with a reciprocating table, a plain or string fixture can be provided. A drill grinding attachment is an obvious example of a standard fixture used for drilling geometry grinding.
Whatever type of fixture is used for grinding, it should have provisions for coolant supply and exit, mounting of wheel dressers, and, if it is a rotating fixture, it should be properly balanced.
These types of fixtures may be the standard work-holding devices, such as mandrels, chucks, chuck with shaped jaws, magnetic chucks, etc.
6. Tapping Fixtures
Tapping fixtures are specially designed to position and securely secure identical work-pieces for cutting internal threads in drilled holes. Oddly shaped and unbalanced components will always necessitate the use of such fixtures, especially if the tapping operation is to be repeated on a mass scale on such parts.
7. Duplex Fixtures
It is the name given to the fixture that holds two similar components at the same time and allows them to be machined at two separate stations at the same time. While a single workpiece is machined at a single station.

Both operations may be similar or dissimilar depending on the requirement. When the machining at both stations is completed, the fixture is indexed through 180 degrees, transferring the first component to the second station for the second operation and the finished component to the first station.
The completed component is then uploaded here, replaced with a new component, and the first operation is performed on it. The cycle is repeated indefinitely, allowing for relatively high-speed mass production of components.
8. Welding Fixtures
Welding fixtures which are are carefully designed for holding and supporting the various components to be welded in their proper locations while preventing distortions in welded structures.
For this, the locating element must be carefully placed; clamping must be light but firm, and clamping elements must be placed clear of the welding area. To withstand the welding stresses, the fixture must be quite stable and rigid.
9. Assembly Fixtures
The purpose of Assembly fixtures is to hold various components together in their proper relative position during assembly. Two or more steel plates, for example, can be held together in relative positions and riveted.
Mechanical assembly fixtures are those that are used to hold components while performing mechanical operations. In contrast, there are other types of fixtures in which the components are held for joining, such as welding fixtures, which are also assembly fixtures, but only for hot joining.
10. Indexing Fixtures

Several components must be machined on various surfaces so that their machined surface surfaces or forms are evenly spaced. Such elements must be indexed in the same number as the number of surfaces to be machined. The holding devices (jigs or fixtures) used are designed to accommodate an indexing mechanism. An indexing fixture is a fixture that contains such a device.
Principles of Jigs and Fixtures
The successful designing of a jig or a fixture depends upon the analysis of several factors which must be carefully studied before the actual work is taken in hand. The following are the essential factors which must be considered in designing a jig or a fixture :
1. Study of the component.
2. Study of the type and capacity of the machine.
3. Study of the locating elements.
4. Study of the loading and unloading arrangement.
5. Study of the clamping arrangement.
6. Study of the power devices for operating the clamping elements.
7. Study of the clearance required between the jig and the component.
8. Study of the indexing devices.
9. Study of the tool guiding and cutter setting elements.
10. Study of the fool-proofing arrangement.
11. Study of the ejecting devices.
12. Study of the swarf removal arrangement.
13. Study of the rigidity and vibration program.
14. Study of the table fixing arrangement.
15. Study of the safety devices.
16. Study of the methods of manufacture of the jig base, body or frame.
Advantages of Jigs and Fixtures
The following are the advantages of employing jigs and fixtures in mass producing work.
1. It eliminates the marking out, measuring, and other setting methods before machining.
2. It increases the machining accuracy, because the workpiece is automatically located and the tool is guided without making any manual adjustment.
3. It enables production of identical parts which are interchangeable. This facilitates the assembly operation.
4. It increases the production capacity by enabling a number of workpieces to be machined in the single set up, and in some cases a number of tools may be made to operate simultaneously. The handling time is so greatly reduced due to heat setting and locating of the work. The speed, feed and depth of cut for machining can be increased due to high clamping rigidity of jigs and fixtures.
5. It reduces the operator’s labour and consequent fatigue as the handling operations are minimized and simplified.
6. It reaches semi-skilled operator to perform the operations as the setting operations of the tool and the work are mechanized. This saves labour cost.
7. It reduces the expenditure on the quality control of the finished products.
8. It reduces the overall cost of machining by fully or partly automatizing the processes.
Disadvantages of Jigs and Fixtures
- It is possible that it will deteriorate over time.
- Another is the high initial setup costs (and time).
- And it can use a lot of material and be bulky.
Applications of Jigs and Fixtures
- For the mass production of the parts of automobile.
- Inspection of the part in continuous production in the manufacturing industries.
- Cutting ingots in steel plant.
- In refrigeration industry ,it ise used.
- In Pump assembling process,it is used.
- For drilling flanges & drilling the holes to any required angles.
- For multi-spindle machining.
- Jigs are used for mass drilling, reaming and tapping.
- To guide the tools for machining contours.
- Fixtures used for milling, mass turning, and the grinding operations.
Materials used for Jigs and Fixtures
The following materials are used to make Jigs and Fixtures:
- Hardened steel
- Grey cast iron
- Plastic
- Carbide
- Epoxy resins
- Stainless steel
- Bronze
- Low melt alloy steel
So we have covered all the things related to jigs and fixtures including elements, types, advantages, disadvantages, and materials used for jigs and fixtures.
If you liked the article please share it with your friends and give your feedback in the comment section.
FAQ (Frequently Asked Questions )
What is jigs & fixture?
Jigs and fixtures are manufacturing equipment used to create components that are interchangeable and similar.
Check Out Other Important Topics
Foundry Tools And Equipment – List, Names & Images
Sand Testing Methods – Full Process
Types of Casting Defects – Complete Overview
Moulding Sand – Properties, Types, Process, MCQs
Plant Layout – Types, Objectives, Principles, Advantages
| IC Engine | Important PDFs | Boilers | Synergy Maritime Exam | Naval Arch | MEO Class 4 |
| Interview Questions | Difference Between | Types of Pumps | Auxiliary Machines | Types of Valves | Home |